Developing a standard for authenticating halal gelatine catfish skin: A study on the effect of periodization quarantine (istihalah) on gelatin quality in catfish fed with pig-contaminated feeds
Abstract
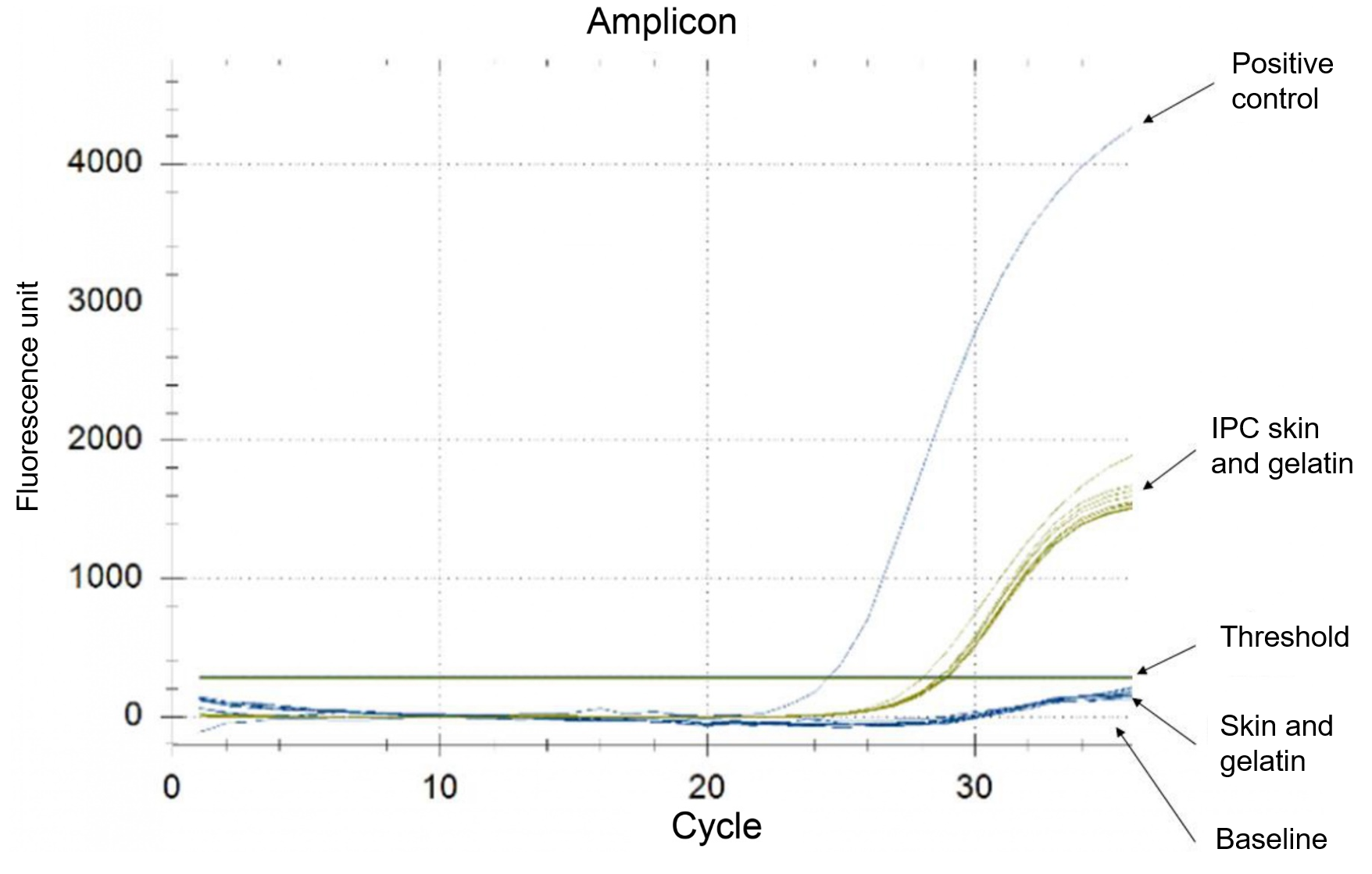
The search for sustainable feed alternatives has led to exploring unconventional sources, including food waste, amidst the growing demand for halal gelatin, which has created a significant need for fish skin by-products. Therefore, this study aimed to authenticate the halal status of catfish skin gelatin by verifying feed origin and determining the contents of pig contaminants. Halal standard was verified using a specific DNA analysis of pig components, conducted at each stage, including feed containing pig, fish skin, and catfish gelatin. Gelatin in catfish skin was predominantly composed of amino acids glycine and proline, and fish enlargement stage which led to a skin yield of 5.36 ± 0.75%. Furthermore, the yields of gelatin were 8.67%, 9.94%, and 9.19%, with gel strengths of 133.4 ± 1.2, 129.9 ± 1.4, and 121.9 ± 2.8 bloom, respectively, for the different quarantine periods. The characterization of gelatin using FTIR showed the presence of functional groups, such as amide A, I, II, and III. Real-time PCR detected the presence of pig DNA in feed but not in catfish skin or gelatin. In conclusion, a quarantine period of 0 days for catfish fed pig-containing feed was sufficient to cleanse catfish skin of pig contaminants, with no indication of pig DNA being found.
References
Agustono. Pengukuran kecernaan protein kasar, serat kasar, lemak kasar, BETN, dan energi pada pakan komersial ikan gurami (Osphronemus gouramy) dengan menggunakan teknik pembedahan. Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan Dan Kelautan. 2014;6(1):71-79. https://doi.org/10.20473/jipk.v6i1.11384
Alfia AR, Arini E, Elfitasari E. Pengaruh Kepadatan yang Berbeda Terhadap Kelulusanhidupan dan Pertumbuhan Ikan Nila (Oreochromis niloticus) pada Sistem Resirkulasi dengan Filter Bioball. Journal of Aquaculture Management and Technology. 2013;2(3):86-93.
Arnesen JA, Gildberg A. Extraction of muscle proteins and gelatine from cod head. Process Biochemistry. 2006;41(3):697-700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2005.09.001
Arnesen JA, Gildberg A. Extraction and characterisation of gelatine from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) skin. Bioresource Technology. 2007;98(1):53-57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.11.021
Az-Zuhaili W. Fiqih Islam Wa Adillatuhu. 2011. Jakarta: Gema Insani.
Azilawati MI, Hashim DM, Jamilah B, Amin I. RP-HPLC method using 6-aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate incorporated with normalization technique in principal component analysis to differentiate the bovine, porcine and fish gelatins. Food Chemistry. 2015;172:368-376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.09.093
Cebi N, Durak MZ, Toker OS, Sagdic O, Arici M. An evaluation of Fourier transforms infrared spectroscopy method for the classification and discrimination of bovine, porcine and fish gelatins. Food Chemistry. 2016;190:1109-1115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.06.065
Chang PH, Chang PH, Kuo ST, Chen MH, Tu C, Huang SH, Lai TM, Yu WC. Jaundice in cultured hybrid catfish, Clarias betrachus x Clarias fuscusi. Journal of Veterinary and Clinical Science. 2008;1(2):47-51.
Cheng Z, Mo WY, Man YB, Nie XP, Li KB, Wong MH. Replacing fish meal by food waste in feed pellets to culture lower trophic level fish containing acceptable levels of organochlorine pesticides: Health risk assessments. Environment International. 2014;73:22-27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2014.07.001
FAO. Fisheries and Aquaculture Department. The state of world fisheries and aquaculture. Contributing to food security and nutrition for all, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. 2016. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
Hafidz RMRN, Yaakob CM, Amin I, Noorfaizan A. Chemical and functional properties of bovine and porcine skin gelatin. International Food Research Journal. 2011;18(2):787-791.
Haetami K, Junianto J, Iskandar I, Rostika R, Abun A. Durability and Water Stability of Pellet Fish Supplementation Results pairing Coconut Oils and Hazlenut Oil. International Journal of Environment, Agriculture and Biotechnology. 2017;2(3):1336-1340. https://doi.org/10.22161/ijeab/2.3.40
Hashim DM, Man YBC, Norakasha R, Shuhaimi M, Salmah Y, Syahariza ZA. Potential use of Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy for differentiation of bovine and porcine gelatins. Food Chemistry. 2010;118(3):856-860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.05.049
Hossain MAR, Haylor GS, Beveridge MCM. The influence of food particle size on gastric emptying and growth rates of fingerling African catfish, Clarias gariepinus Burchell, 1822. Aquaculture Nutrition. 2000;6(2):73-76. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2095.2000.00131.x
Jamilah B, Harvinder KG. Properties of gelatins from skins of fish-Black tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) and red tilapia (Oreochromis nilotica). Food Chemistry. 2002;77(1):81-84. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-8146(01)00328-4
Jónsson Á, Finnbogadóttir GA, Þorkelsson G, Magnússon H, Reykdal Ó, Arason S. Dried fish as health food: Report. Matis Food Research. Innovation and Safety. 2007:1-6.
Karim AA, Bhat R. Fish gelatin: properties, challenges, and prospects as an alternative to mammalian gelatins. Food Hydrocolloids. 2009;23(3):563-576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2008.07.002
Kong J, Yu S. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic analysis of protein secondary structures. Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica. 2007;39(8):549-559. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7270.2007.00320.x
Liu H, Li D, Guo S. Rheological properties of channel catfish (Ictalurus punctaus) gelatine from fish skins preserved by different methods. LWT-Food Science and Technology. 2008;41(8):1425-1430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2007.09.006
Man YC, Aida AA, Raha AR, Son R. Identification of pork derivatives in food products by species-specific polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for halal verification. Food Control. 2007;18(7):885-889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2006.05.004
Marine and Fisheries Ministry. Kelautan dan Perikanan dalam Angka 2015. Pusat Data, Statistik dan Informasi. 2015.
Marine and Fisheries Ministry. Petunjuk Teknis Penyaluran Bantuan Gerakan Pakan Ikan Mandiri Tahun 2018. 2018.
Mostafa AG, Shaltout OE, Abdallah AE, Osheba AS. Physicochemical characteristics of gelatin extracted from catfish (Clarias gariepinus) and carp (Cyprinus carpio) skins. Middle East Journal of Agriculture Research. 2015;04(02):359-372.
Muyonga JH, Cole CGB, Duodu KG. Extraction and physicochemical characterisation of Nile perch (Lates niloticus) skin and bone gelatin. Food Hydrocolloids. 2004;18(4):581-592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2003.08.009
National Standardization Agency. SNI 01-4087-2006. Pakan buatan untuk ikan lele dumbo (Clarias gariepinus) pada budidaya intensif. 2006. Jakarta: Badan Standardisasi Nasional.
Sabiq S. Fiqih Sunnah Jilid 4. 2006. Jakarta: Pena Pundi Aksara.
Wan Norhana MN, Dykes GA, Padilah B, Ahmad Hazizi AA, Masazurah AR. Determination of quarantine period in African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) fed with pig (Sus sp.) offal to assure compliance with halal standards. Food Chemistry. 2012;135(3):1268-1272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.05.083
Widyaninggar A, Triwahyudi, Triyana K, Rohman A. Differentiation between porcine and bovine gelatin in commercial capsule shells based on amino acid. Indonesia Journal Pharmacy. 2012;23(2):96-101.
Copyright (c) 2023 Bambang Riyanto, Dinamella Wahjuningrum, Wahyu Ramadhan, Muhammad Umar Al Faruqi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.











