Comparison of buried continuous intradermal and simple interrupted suture patterns for skin closure in feline ovariohysterectomy
Abstract
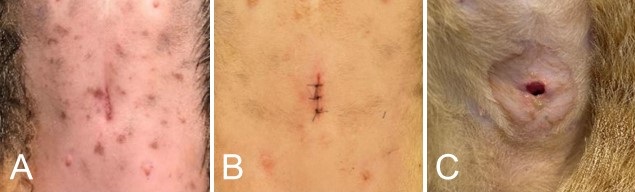
Ovariohysterectomy is widely performed in small animals and is often complicated by wound dehiscence. This study evaluated two suture techniques, buried continuous intradermal (BCID) and simple interrupted (SI), in 42 female cats using nonabsorbable nylon sutures. Weight, incision length, suture length, and closure time were also analysed. Postoperative assessments at 18-24 h and 5-7 d included monitoring for swelling, erythema, exudate, and dehiscence. The results indicated a significantly higher incidence of complications, notably dehiscence, in the SI group. Consequently, BCID is recommended because of its lower complication rate and reduced risk of infection from self-trauma
Downloads
References
AbdelKhalek AS, Youssef HA, Ali MF, Ali MM, Abdel Hakiem MAH, Mahmoud HFF. 2019. An assessment of clinical, biometric, cosmetic and microscopic outcomes of four suture techniques for cutaneous closure of laparotomy wounds: an experimental study in rabbits. Journal of Dairy Veterinary & Animal Research. 8(1):42-53. https://doi.org/10.15406/jdvar.2019.08.00241
Burrow R, Shaver SL, Holmes JH. 2023. Outcomes of elective gonadectomy procedures performed on dogs and cats by veterinary students and shelter veterinarians in a shelter environment. Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association. 253(10):1294-1299. https://doi.org/10.2460/javma.253.10.1294 | PMid:30398427
DeTora M, McCarthy RJ. 2011. Commentary ovariohysterectomy versus ovariectomy for elective sterilization of female dogs and cats: is removal of the uterus necessary? Journal of the American Veterinary Medicine Association. 239(11):1409-1412. https://doi.org/10.2460/javma.239.11.1409 | PMid:22087712
Griffon DJ, Hamaide A. 2015. Chapter 9: Dehiscence, Complications in small animal surgery. Wiley-Blackwell. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119421344
Höer J, Klinge U, Schachtrupp A, Töns C, Schumpelick V. 2001. Influence of suture technique on laparotomy wound healing: an experi-mental study in the rat. Langenbeck's archives of surgery. 386:218-223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004230000196 | PMid:11382325
Hohenleutner U, Egner N, Hohenleutner S, Landthaler M. 2000. Intradermal buried vertical mattress suture as sole skin closure: evaluation of 149 cases. Acta Dermato Venereologica. 80(5):344-347. https://doi.org/10.1080/000155500459277 | PMid:11200831
Root Kustritz MV. 2012. Effects of surgical sterilization on canine and feline health and on society. Reproduction in domestic animals= Zuchthygiene. 47(4): 214-222. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0531.2012.02078.x | PMid:22827373
Sylvestre A, Wilson J, Hare J. 2002. A comparison of 2 different suture patterns for skin closure of canine ovariohysterectomy. The Canadian Veterinary Journal. 43(9):699.
Townsend CM, Towsend JrCM, Beauchamp JrRD, Beauchampp RD, Mattox KL, Evers BM, MattoxJr K. 2017. Sabiston textbook of surgery. 20th ed. Philadelphia (US): Elsevier.
Copyright (c) 2024 CC-BY-SA

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).

.jpg)















