Observation of infant body weight and physiological conditions of Siamang (Symphalangus syndactylus) in ex situ conservation
Abstract
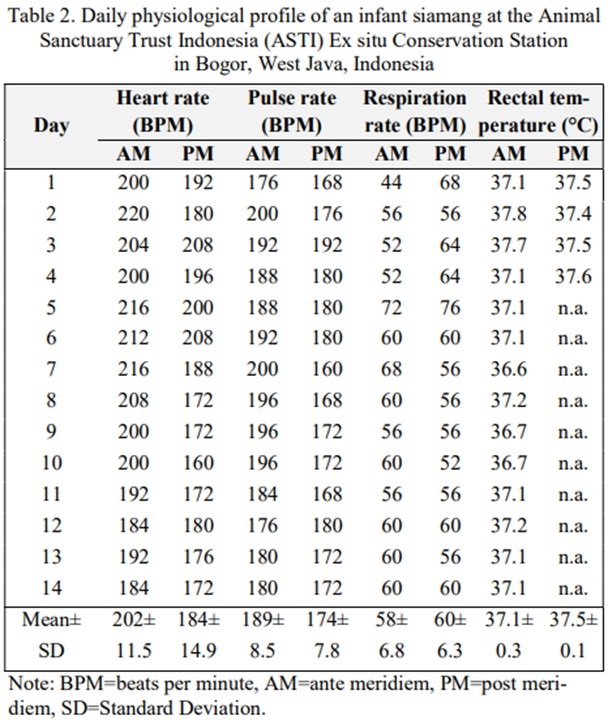
The purpose of this study was to describe the infant body weight and physiological parameters of a Siamang (Symphalangus syndactylus) treated at an ex situ conservation station. This study used an infant Siamang, which was estimated to be ± 3 months old. Body weight parameters were determined based on weekly weight gain for one month. The physiological parameters measured were the heart rate, pulse rate, respiration rate, and rectal temperature. Physiological parameters were measured in the morning and evening for 14 d. The results showed that the average heart rate of infant in the morning was 202±11.5 BPM and in the afternoon was 184±14.9 BPM, the average pulse rate in the morning was 189±8.5 BPM and the afternoon was 174±7.8 BPM, the average respiration rate in the morning was 58±6.8 breaths per minutes and in the afternoon was 60±6.3 breaths per minutes, and the average rectal temperature in the morning was 37.1°C and 37.6°C in the afternoon. The body weight and physiology of the infant were good.
Downloads
References
Dharmalingam S. 2015. Temperature management in infant orangutan (Pongo pygmaeus) at Orangutan Island, Bukit Merah, Perak, Malaysia. Meerit Research Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences. 3(11):497-501
Fleisher GR, Ludwig S, Silverman BK. 2002. Synopsis of Pediatric Emergency Medicine. 4th ed. Philadelpia (US): Lippincott Williams and Wilkins.
Gage LJ. 2002. Hand-Rearing Wild and Domestic Mammals. Iowa (US): Blackwell Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470385005
Lappan S. 2008. Male care of infants in a siamang (Symphalangus syndactylus) population including socially monogamous and polyandrous groups. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. 62:1307-1317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00265-008-0559-7
Nakayama S, Koie H, Pai C, Fujishiro YI, Kanayama K, Sankai T, Yasutomi Y, Ageyama N. 2020. Echocardiographic evaluation of cardiac function in cynomolgus monkeys over a wide age range. Experimental Animal. 69(3):336-344. https://doi.org/10.1538/expanim.19-0128 | PMid:32173671 PMCid:PMC7445060
Sari SRPW, Suartha IN, Batan IW. 2016. Status praesen pedet sapi bali. Buletin Veteriner Udayana. 8(1):36-43.
Suprayogik A, Alaydrussanu G, Ruhyana AY. 2017. Nilai hematologi, denyut jantung, frekuensi respirasi, dan suhu tubuh ternak sapi perah laktasi di Pangalengan. Jurnal Ilmu Pertanian Indonesia (JIPI). 22(2):127-137. https://doi.org/10.18343/jipi.22.2.127
Supriatna J, Wahyono EH. 2000. Panduan Lapangan Primata Indonesia. Jakarta (ID): Yayasan Obor Indonesia.
Yana Y. 2015. Pola makan bayi 0-12 bulan [Internet]. [Diakses 2023 Ags 1]. Tersedia pada: https://hamil.co.id/bayi/makanan-bayi/pola-makan-ba.
Copyright (c) 2023 CC-BY-SA

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).

.jpg)















