Design and Build Water Quality Monitoring System and Weather Station Based on Industrial Sensors with Modbus RS485 Protocol
Abstract
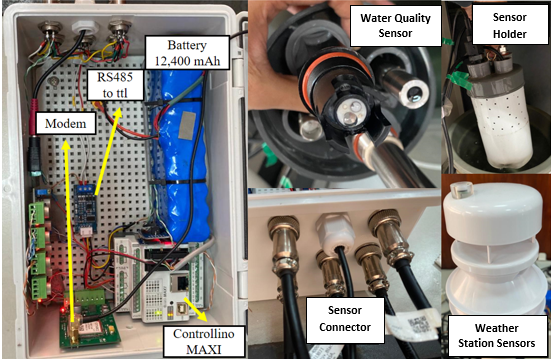
River water quality is typically monitored using sampling methods. This approach makes detecting water pollution challenging owing to the limited sampling time. Another factor influencing water quality is weather, which can be addressed by incorporating weather station sensors as corrective tools. The collected data were processed and visually displayed to make the important information easily interpretable. The water quality parameters measured in this study included Electrical Conductivity (EC), temperature, Total Dissolved Solids (TDS), salinity, pH, turbidity, Dissolved Oxygen (DO), and saturation. The weather parameters measured by the system included wind speed, wind direction, air temperature and humidity, atmospheric pressure, rainfall, and solar radiation. The system's capabilities include data transmission via cellular networks, data backup using an SD card, and industrial sensors with IP (Ingress Protection) standards that utilize the Modbus RS485 protocol. The study followed the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) or waterfall method to ensure system readiness and durability in real-world environments. The Modbus RS485 protocol allows multiple sensors to share a single cable line, resulting in a more efficient and less complex wire arrangement. These findings highlight the necessity of separating sensor lines based on parity type and baud rate for each sensor, enabling simultaneous readings in subsequent operations.
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors submitting manuscripts should understand and agree that copyright of manuscripts of the article shall be assigned/transferred to Jurnal Keteknikan Pertanian. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License (CC BY-SA) where Authors and Readers can copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format, as well as remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, but they must give appropriate credit (cite to the article or content), provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. If you remix, transform, or build upon the material, you must distribute your contributions under the same license as the original.