Performance Evaluation for Surface Run off to Drainage System Normalization at Campus in Jakarta, Indonesia
Abstract
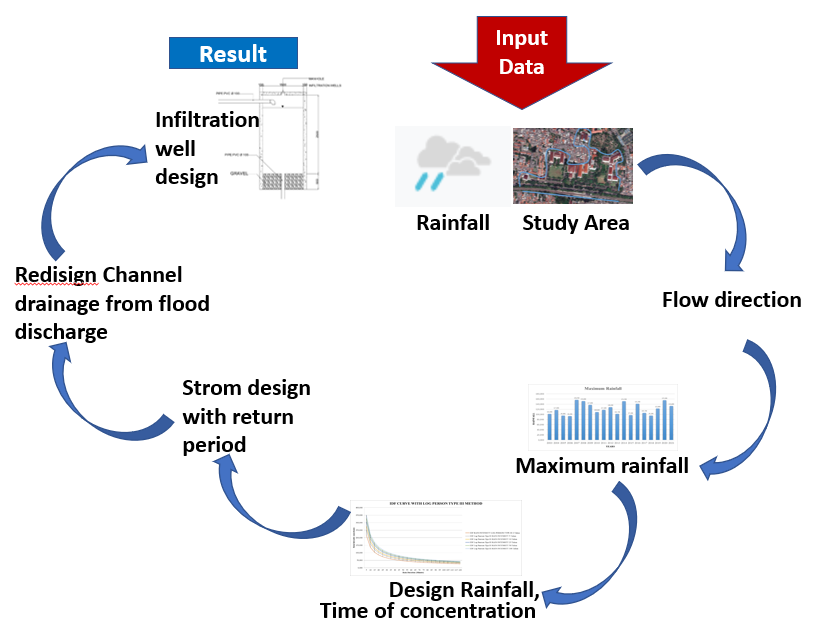
Drainage is an infrastructure that distributesrainwater from one location to another. On the campus of the Faculty of Engineering at Pancasila University, there are several points of water inundation. Several inundation points were identified based on direct monitoring and measurements at the study site. This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of an existing drainage system on campus. The design flood discharge was calculated using a rational method with a five-year return period. From the calculation of hydrology, hydraulics, and comparative analysis of the existing dimensions with the design flood discharge, it was determined that the eight existing channels were unable to accommodate the design flood discharge. Therefore, there are two alternatives for reducing run off discharge. The first is to redesign the drainage channel to improve its size of the drainage channel with a shape that follows the existing shape. The modification involved adjusting the channel height to meet the specified flood discharge requirements. The second alternative was the planning of the infiltration wells. These dimensions are based on the design run off flood discharge, and from the calculation results, the dimensions of the infiltration wells are 1.5 meters in diameter and 2.5 meters high, and four infiltration wells are needed is 4 infiltration wells to reduce the discharge of 1,638 m3/second.
References
Adijaya, K., Prianto, W., & Suripin, S. (2015). Penataan Kanal Banjir Timur Semarang. Jurnal Karya Teknik, 4(March), 313–323. https://ejournal3.undip.ac.id/index.php/jkts/article/view/10246
Ariyani, D., Aprilia, V., Juniati, A. T., Dewi, A. P., & Kurnia, F. (2020). Curve number method to determine the runoff height in the upper Cimanuk watershed. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 852(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/852/1/012020
Ariyani, D., Mohammad Yanuar Jarwadi Purwanto, Euis Sunarti, & Perdinan. (2022). Contributing Factor Influencing Flood Disaster Using MICMAC (Ciliwung Watershed Case Study). Jurnal Pengelolaan Sumberdaya Alam Dan Lingkungan (Journal of Natural Resources and Environmental Management), 12(2), 268–280. https://doi.org/10.29244/jpsl.12.2.268-280
Badan Standarisasi Nasional. 2002. Tata cara perencanaan teknik sumur resapan air hujan untuk lahan pekarangan. Indonesiahlm 1–13.
Budianto, M. B., Yasa, I. W., & Hanifah, L. (2017). Analisis karakteristik curah hujan untuk pendugaan debit puncak dengan metode rasional di Mataram. Spektrum Sipil, 2(2), 137–144.
Buton S, Muharyanto EA. 2021. Evaluation Of Drainage Channel Performance On Clove Flower Street. Uniqbu J. Exact Sci. 2(April):1–7.
David AO, Agunwamba J, Nwaogazie IL. 2019. Development of Models for Rainfall Intensity- duration-frequency for Akure , Development of Models for Rainfall Intensity- duration-frequency for Akure , South-west , Nigeria. Int. J. Environ. Clim. Chang. 9(August):457–466.doi:10.9734/ijecc/2019/v9i830131.
F, B. M., Tazkiaturrizki, T., & Winarni, W. (2019). Analisis Perbandingan Sistem Drainase Konvensional Dan Ecodrainage Di Kawasan Perumahan Citra Maja Raya (Tahap 1), Banten. Seminar Nasional Pembangunan Wilayah Dan Kota Berkelanjutan, 1(1), 213–221. https://doi.org/10.25105/pwkb.v1i1.5279
Fauziyah, S., Sobriyah, & Susilowati. (2013). Analisis Karakteristik dan Intensitas Hujan Kota Surakarta. Matriks Teknik Sipil, 1(1), 82–89.
Fraiture C De, Susanto RH, Suryadi FX, Wahyu HMH. 2017. Urban Drainage Management and Flood Control Improvement Using the Duflow Case Study : Aur Sub Catchment , Palembang , South Sumatra , Indonesia. Makara J. Technol. Vol. 21(2):1–11.doi:10.7454/mst.v21i2.3085.
Francisco THS, Menezes OVC, Guedes ALA, Maquera G, Neto DC V., Longo OC, Chinelli CK, Soares and CAP. 2023. The Main Challenges for Improving Urban Drainage Systems from the Perspective of Brazilian Professionals. infrastructures MDPI. 8(5):1–20.
Guntoro, D. E., Harisuseno, D., & Cahya, E. N. (2017). Pengelolaan Drainase Secara Terpadu Untuk Pengendalian Genangan Di Kawasan Sidokare Kabupaten Sidoarjo. Jurnal Tenik Pengairan, 008(01), 60–71. https://doi.org/10.21776/ub.jtp.2017.008.01.06
Halim, F. (2014). Pengaruh Hubungan Tata Guna Lahan Dengan Debit Banjir Pada Daerah Aliran Sungai Malalayang. Jurnal Ilmiah Media Engineering, 4(1), 45–54.
Imamuddin, M., & Antoni, H. (2019). Analisis Kapasitas Drainase Jalan Panjang Sampai Dengan Rumah Pompa Kedoya Utara. Prosiding Semnastek, 1–6.
Kimi, S. (2015). Pengaruh Jenis Dan Kemiringan Dasar Saluran Terhadap Nilai Koefisien C Dengan Persamaan Manning Berdasarkan Hasil Uji Laboratorium. Jurnal Penelitian Dan Kajian Teknik Sipil, 4(1), 1–4.
Lestari, L. B., Mayang, A. Y., Budieny, H., & Darsono, S. (2017). Perencanaan Sistem Drainase Kabupaten Magelang. Jurnal Karya Teknik Sipil, 6(1), 356–365.
Lubis, F. (2016). Analisa Frekuensi Curah Hujan Terhadap Kemampuan Drainase Pemukiman Di Kecamatan Kandis. Siklus: Jurnal Teknik Sipil, 34–46. https://journal.unilak.ac.id/index.php/SIKLUS/article/view/293
Mulyono, D. (2016). Analisis Karakteristik Curah Hujan Di Wilayah Kabupaten Garut Selatan. Jurnal Konstruksi, 12(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.33364/konstruksi/v.12-1.274
Nugroho, D., Leksono, B., & Sholikhah, I. (2021). Perencanaan Ulang Sistem Saluran Drainase di Kecamatan Menganti Kabupaten Gresik. Jurnal Wahana Teknin, 10(1), 15–22. Drainase; Debit Rencana; Saluran Bentuk Persegi; Pasangan Batu; Beton Precast; Pola Jaringan Drainase Siku
Nurhamidin, A. E., Jasin, M. I., & Halim, F. (2015). Analisis Sistem Drainase Kota Tondano (Studi Kasus Kompleks Kantor Bupati Minahasa). Jurnal Sipil Statik, 3(9), 599–612. https://ejournal.unsrat.ac.id/index.php/jss/article/view/9815
Pitaloka, M. G., & Lasminto, U. (2017). Perencanaan Sistem Drainase Kebon Agung Kota Surabaya, Jawa Timur. Jurnal Teknik ITS, 6(1), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.12962/j23373539.v6i1.21425
Purnama, A., & Saputri, D. E. (2016). Studi Kelayakan Saluran Drainase Jalan Sultan Kaharuddin Km. 02 Kabupaten Sumbawa. Jurnal SAINTEK UNSA, 1(1), 1–19.
Rifqi, P. M., Setyowati, D. L., & Suroso, S. (2017). Analisis Spasial Debit Puncak Daerah Aliran Sungai Beringin dengan Metode Rasional. Geo-Image, 6(1). https://journal.unnes.ac.id/sju/index.php/geoimage/article/view/15245%0Ahttps://journal.unnes.ac.id/sju/index.php/geoimage/article/view/15245/8251
Suadnya, D., Sumarauw, J., & Mananoma, T. (2017). Analisis Debit Banjir Dan Tinggi Muka Air. Jurnal Sipil Statik, 5(3), 143–150. https://ejournal.unsrat.ac.id/index.php/jss/article/view/29979
Sucipto, & Sutarto, A. (2007). Analisis Kapasitas Tampungan Sistem Drainase Kali Beringin Untuk Pengendalian Banjir Wilayah Drainase Semarang Barat. Jurnal Teknik Sipil & Perencanaan, Volume 9, 33–42.
Suryaman, H. (2013). Evaluasi Sistem Drainase Kecamatan Ponorogo Kabupaten Ponorogo. Jurnal Penelitian, 02(1), 0–07.
Suryanti, I., Norken, I. N., & Sila Dharma, I. G. B. (2013). Kinerja Sistem Jaringan Drainase Kota Semarapura Di Kabupaten Klungkung. Jurnal Spektran, 1(1), 30–34. https://doi.org/10.24843/spektran.2013.v01.i01.p05
Widasmara, M. Y., & Hadi, M. P. (2016). Pemodelan Debit Aliran DAS Bompon Menggunakan Metode Rasional Modifikasi. Jurnal Bumi Indonesia, 1–13.
Wijesekera SNT. 2017. Preparation of the Stormwater Drainage Management Plan for Matara Municipal Council. ENGINEER. 44(3):11–29.doi:10.4038/engineer.v44i3.6961.
Wismarini, T. D., & Ningsih, D. H. U. (2010). Analisis Sistem Drainase Kota Semarang Berbasis Sistem Informasi Geografi dalam Membantu Pengambilan Keputusan bagi Penanganan Banjir. Jurnal Teknologi Informasi DINAMIK, XV(1), 41–51.
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).