Wildlife Trade Governance and Zoonosis: Missing Link From Forest to Market Place
Abstract
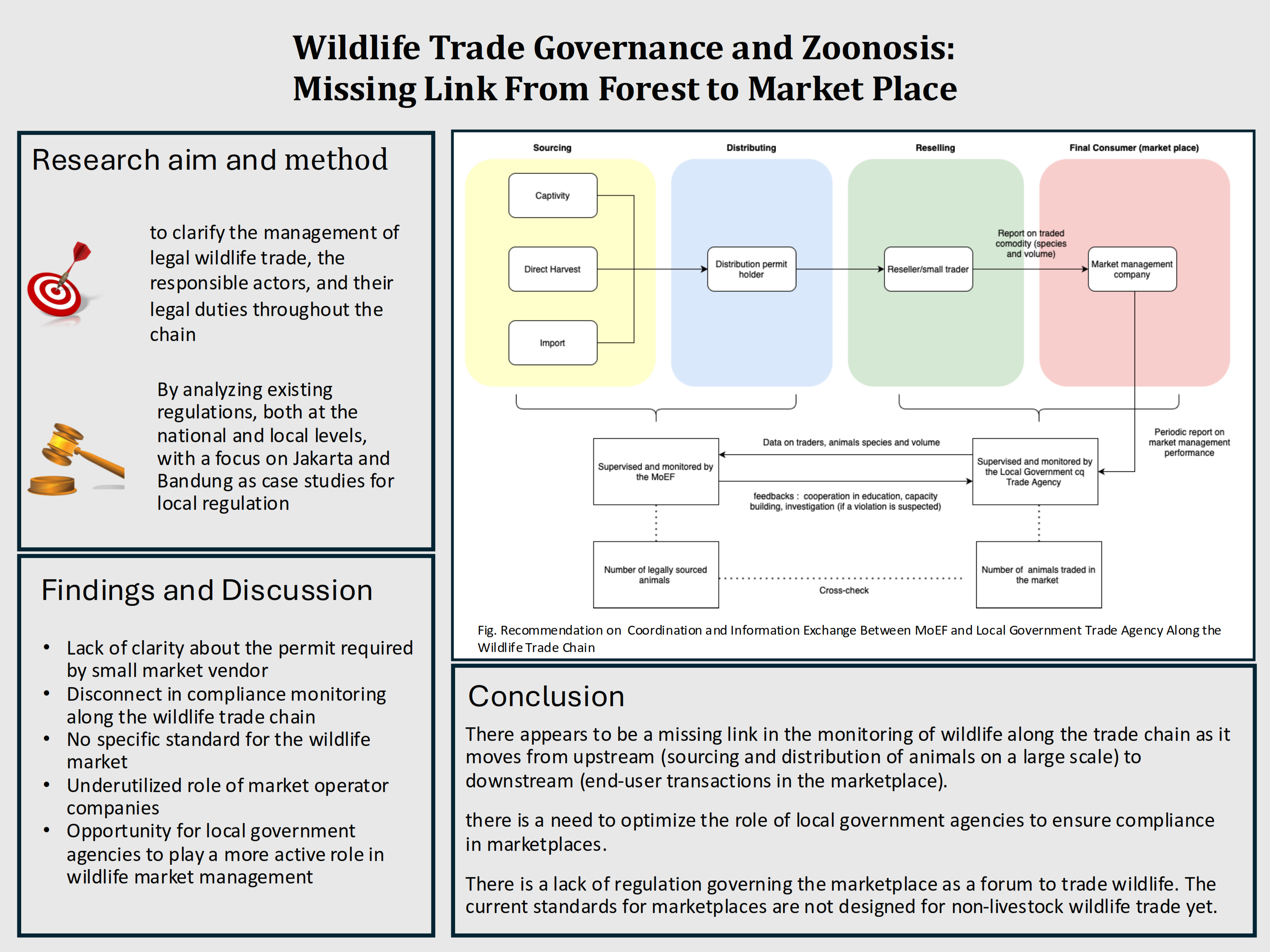
Indonesia is a major hub for domestic and international wildlife trade. Illegal and unregulated trade threatens species survival and public health through potential zoonotic disease transmission. Effective governance, including strengthened legislation and enforcement, is essential to address these issues. This paper scrutinizes the laws and policies governing wildlife trade and zoonosis prevention in Indonesia, spotlighting the regulatory path from source to marketplace transactions. By analyzing existing regulations, both at the national and local levels, with a focus on Jakarta and Bandung as case studies for local regulation, this study aims to clarify the management of legal wildlife trade, the responsible actors, and their legal duties throughout the chain. The findings underscore a disconnect exists between upstream monitoring and downstream marketplace activities. Furthermore, the discussion reveals a critical regulatory loophole- the lack of regulations addressing standards for a healthy non-livestock wildlife market and the often-overlooked role of local government agencies, which, despite playing a marginalized role in wildlife trade monitoring strategies, are the forefront of zoonosis surveillance and monitoring duty.
Full text article
References
2. Jepson, P.; Ladle, R. Bird-Keeping in Indonesia: Conservation Impacts and the Potential for Substitution-Based Conservation Responses. Oryx 2005, 39.
3. Chng, S.C.L.; Eaton, J.A.; Krishnasamy, K.; Shepherd, C.R.; Nijman, V. In the Market for Extinction: An Inventory of Jakarta’s Bird Markets; TRAFFIC: Petaling jaya, Malaysia, 2015;
4. Marshall, H.; Collar, N.J.; Lees, A.C.; Moss, A.; Yuda, P.; Marsden, S.J. Characterizing Bird-Keeping User-Groups on Java Reveals Distinct Behaviours, Profiles and Potential for Change. People and Nature 2020, 2, 877–888, doi:10.1002/pan3.10132.
5. Supangkat, B.; Iskandar, J.; Partasasmita, R. Hobby and Business on Trading Birds: Case Study in Bird Market of Sukahaji, Bandung, West Java and Splendid, Malang, East Java (Indonesia). Biodiversitas 2019, 20, 1316–1332, doi:10.13057/biodiv/d200522.
6. MoEF Regulation No. P.106 Year 2018 on Second Revision on MoEF Regulation No P.20 on the List of Protected Plants and Animals;
7. Eaton, J.A.; Eaton, J.A.; Shepherd, C.R.; Rheindt, F.E.; Harris, J.B.C.; Balen, B. van; Wilcove, D.S.; Collar, N.J. Trade-Driven Extinctions and near-Extinctions of Avian Taxa in Sundaic Indonesia. Forktail 2015, 31, 1--12.
8. Government Regulation No. 8 Year 1999 on Utilisation of Wild Plant and Animal;
9. The Illegal Wildlife Trade in Southeast Asia: Institutional Capacities in Indonesia, Singapore, Thailand and Viet Nam | En | OECD Available online: https://www.oecd.org/gov/the-illegal-wildlife-trade-in-southeast-asia-14fe3297-en.htm (accessed on 10 June 2024).
10. Nijman, V.; Morcatty, T.Q.; Feddema, K.; Campera, M.; Nekaris, K. a. I. Disentangling the Legal and Illegal Wildlife Trade–Insights from Indonesian Wildlife Market Surveys. Animals 2022, 12, 628, doi:10.3390/ani12050628.
11. Morcatty, T.Q.; Pereyra, P.E.R.; Ardiansyah, A.; Imron, M.A.; Hedger, K.; Campera, M.; Nekaris, K.A.-I.; Nijman, V. Risk of Viral Infectious Diseases from Live Bats, Primates, Rodents and Carnivores for Sale in Indonesian Wildlife Markets. Viruses 2022, 14, 2756, doi:10.3390/v14122756.
12. Nijman, V.; Morcatty, T.; Smith, J.; Atoussi, S.; Shepherd, C.; Siriwat, P.; Nekaris, K.A.; Bergin, D. Illegal Wildlife Trade – Surveying Open Animal Markets and Online Platforms to Understand the Poaching of Wild Cats. Biodiversity 2019, 20, 1–4, doi:10.1080/14888386.2019.1568915.
13. t Sas-Rolfes, M.; Challender, D.; Hinsley, A.; Verissimo, D.; Milner-Gulland, E. Illegal Wildlife Trade: Patterns, Processes, and Governance. Annual Review of Environment and Resources 2019, 44, 1–28, doi:10.1146/annurev-environ-101718-033253.
14. Biggs, D.; Peel, A.J.; Astaras, C.; Braczkowski, A.; Cheung, H.; Choi, C.-Y.; Orume, R.D.; Cáceres-Escobar, H.; Phelps, J.; Plowright, R.K.; et al. Governance Principles for the Wildlife Trade to Reduce Spillover and Pandemic Risk. CABI One Health 2023, 2023, ohcs202300013, doi:10.1079/cabionehealth.2023.0013.
15. Roe, D.; Dickman, A.; Kock, R.; Milner-Gulland, E.J.; Rihoy, E.; ’t Sas-Rolfes, M. Beyond Banning Wildlife Trade: COVID-19, Conservation and Development. World Dev 2020, 136, 105121, doi:10.1016/j.worlddev.2020.105121.
16. Eskew, E.A.; Carlson, C.J. Overselling Wildlife Trade Bans Will Not Bolster Conservation or Pandemic Preparedness. The Lancet Planetary Health 2020, 4, e215–e216, doi:10.1016/S2542-5196(20)30123-6.
17. Bashyal, R.; Paudel, K.; Hinsley, A.; Phelps, J. Making Sense of Domestic Wildlife and CITES Legislation: The Example of Nepal’s Orchids. Biological Conservation 2023, 280, 109951, doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2023.109951.
18. Pascual, M.; Wingard, J.; Bhatri, N.; Rydannykh, A.; Phelps, J. Building a Global Taxonomy of Wildlife Offenses. Conservation Biology 2021, 35, 1903–1912, doi:10.1111/cobi.13761.
19. Latinne, A.; Saputro, S.; Kalengkongan, J.; Kowel, C.L.; Gaghiwu, L.; Ransaleleh, T.A.; Nangoy, M.J.; Wahyuni, I.; Kusumaningrum, T.; Safari, D.; et al. Characterizing and Quantifying the Wildlife Trade Network in Sulawesi, Indonesia. Global Ecology and Conservation 2020, 21, e00887, doi:10.1016/j.gecco.2019.e00887.
20. Maulany, R.; Mutmainnah, A.; Nasri, N.; Achmad, A.; Ngakan, P. Tracing Current Wildlife Trade: An Initial Investigation in Makassar City, Indonesia. Forest and Society 2021, 5, 277–287, doi:10.24259/fs.v5i2.9097.
21. Nijman, V. Illegal Trade in Indonesia’s National Rare Animal Has Moved Online. Oryx 2020, 54, 12–13, doi:10.1017/S0030605319001157.
22. Government Regulation No. 5 Year 2021 on Risk-Based Business Permit;
23. Law No. 11 Year 2020 on Job Creation;
24. MoEF Regulation No. 3 Year 2021 on Standard for Business Activities in Implementation of Risk-Based Permits in Environment and Forestry Sector;
25. MoEF Regulation No. 4 Year 2021 on List of Activities That Requires Amdal, UKL-UPL or SPPLH.;
26. Phelps, J.; Biggs, D.; Webb, E.L. Tools and Terms for Understanding Illegal Wildlife Trade. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 2016, 14, 479–489, doi:10.1002/fee.1325.
27. Ministry of Trade Regulation No. 21 Year 2021 on Guidelines for Development and Management of Trade Facilities;
28. Ministry of Cooperative, Small Scale and Medium Scale Business Regulation No. 7 Year 2022 on The Implementation of Public Market Revitalitation Managed by Cooperative Funded by State Budget;
29. Jakarta Regulation No. 2 Year 2018 on Market Management;
30. Jakarta Regulation No. 3 Year 2018 on Perumda Pasar Jaya;
31. Bandung City Regulation No. 8 Year 2020 on Perumda Pasar Juara Kota Bandung;
32. Ministry of Human Resource Development and Culture Regulation No. 7 Year 2022 on Guideline on Zoonosis and New Infectious Disease Prevention and Control, Tim Koordinasi Pusat Pencegahan Dan Pengendalian Zoonosis Dan Penyakit Infeksius Baru;
33. Government Regulation No. 47 Year 2014 on Animal Disease Control and Mitigation;
34. Ministry of Health Regulation No. 17 Year 2020 on Healthy Market Standard;
35. Ministry of Internal Affairs Regulation No. 101 Year 2018 on Technical Standard for Municipalities Basic Service on Disaster Dealings;
36. President Regulation No 30 Year 2011 on Zoonosis Control;
37. The Online Single Submission Portal.
38. Biggs, D.; Courchamp, F.; Martin, R.; Possingham, H.P. Conservation. Legal Trade of Africa’s Rhino Horns. Science 2013, 339, 1038–1039, doi:10.1126/science.1229998.
39. Phelps, J.; Carrasco, L.R.; Webb, E.L. A Framework for Assessing Supply-Side Wildlife Conservation. Conservation Biology 2014, 28, 244–257, doi:10.1111/cobi.12160.
40. Busilacchi, S.; Butler, J.; van putten, I.; Cosijn, M.; Posu, J.; Fitriana, R.; Slamet, A. Why Does Illegal Wildlife Trade Persist in Spite of Legal Alternatives in Transboundary Regions? Human Dimensions of Wildlife 2021, 27, 1–18, doi:10.1080/10871209.2021.1876963.
41. Kepdirjen Peternakan Dan Kesehatan Hewan No. 5429/KPTS/PK.320/F/05/2022 on SOP Pengendalian Dan Penanggulangan Wabah Penyakit Mulu Dan Kuku (PMK) Di Indonesia;
42. Jakarta Governor Regulation No. 142 Year 2014 on Jakarta Zoonosis Control Commission;
43. MoEF Circular No 251/KSDAE/KKH/KSA.2/3/2020 on Prevention and Control of New Infectious Diseases and Zoonosis.;
44. Jakarta Regulation No. 7 Year 2018 on Pasar Jaya Management and Business Development;
Authors
Copyright (c) 2025 Rika Fajrini, Richard Moore, Wendi Prameswari, Yumni K Ghassani, Jacob Phelps

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Media Konservasi is an open access journal, meaning that all content is freely available without charge to the user or their institution. Users are allowed to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts of the articles in this journal without needing to request prior permission from the publisher or the author.
All articles published by Media Konservasi are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. This allows for unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided proper credit is given to the original authors.
Authors submitting manuscripts should understand and agree that the copyright of published manuscripts is retained by the authors. Copyright encompasses the exclusive rights of authors to reproduce, distribute, and sell any part of the journal articles in all forms and media. Reproduction of any part of this journal, its storage in databases, and its transmission by any form or media is allowed without written permission from Media Konservasi.