Understanding the Household Waste Management: An Application of the Theory of Planned Behavior
Abstract
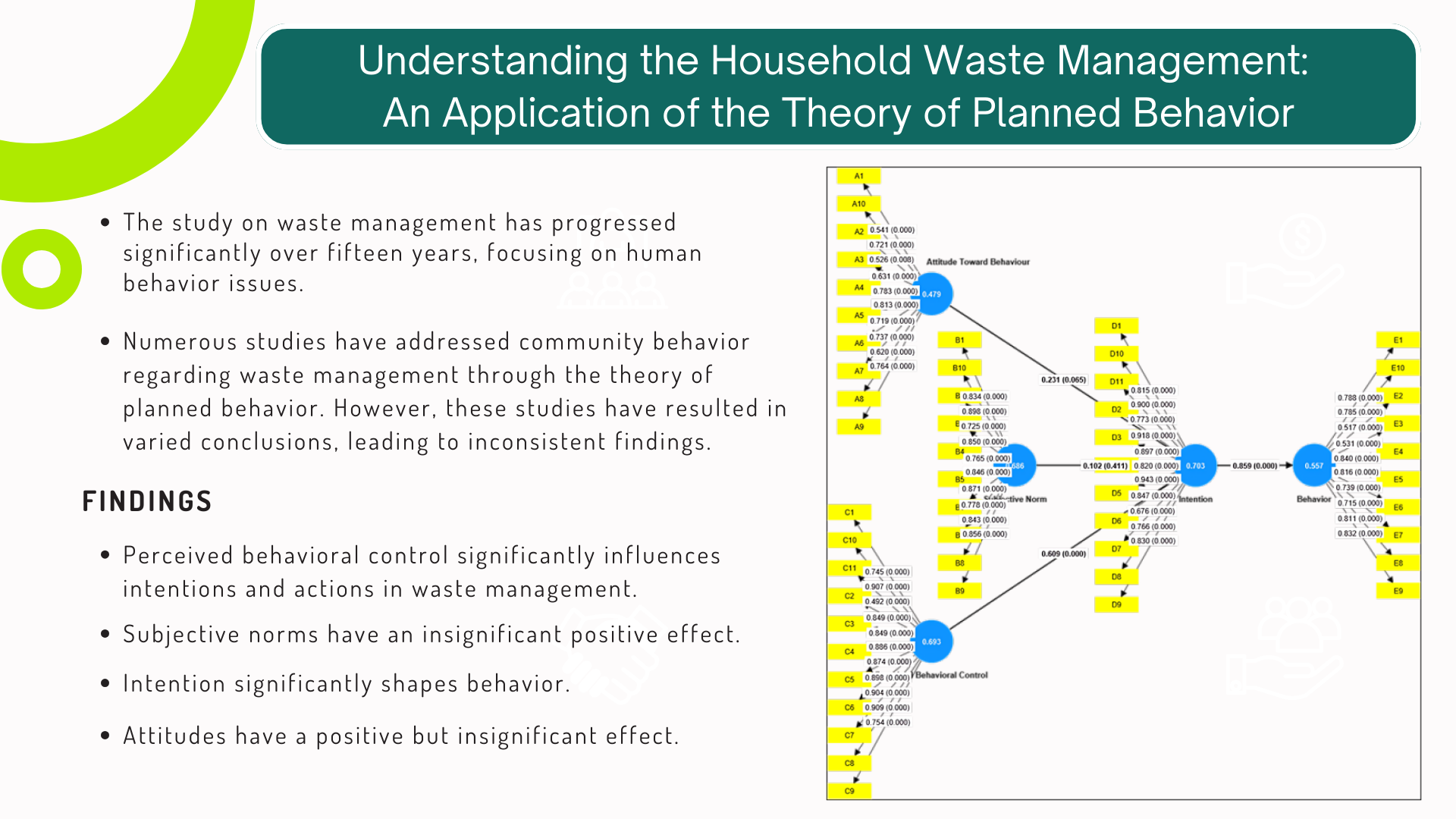
The study of waste research has advanced significantly in over fifteen years, exploring human behavior and the physical aspects of waste. The theory of planned behavior has been extensively utilized to explain the phenomena and symptoms related to behavior related to waste. Consequently, the objective of our study is to apply the theory of planned behavior to enhance our understanding of how households manage waste. This understanding is a critical stage in developing effective strategies and improving the level of quality of existing policy and program intervention. The study is conducted at Tangerang Selatan, a municipality region in Banten Province. Likert scale structured questionnaire instruments are employed for primary data collection, and household samples are chosen based on predetermined characteristics such as domicile and age purposively. A structural equation model based on Smart PLS is employed in the analysis. The results of our study have implications for the development of policies since they encourage the establishment of specialized waste management facilities as well as promote community involvement in residential waste management.
Full text article
References
1. Kementerian Lingkungan Hidup dan Kehutanan. Sistem Informasi Pengelolaan Sampah Nasional: Komposisi Sampah Berdasarkan Sumber Sampah. 2024. Available online: https://sipsn.kemenlh.go.id/sipsn/public/data/sumber (accessed on 01 September 2025).
2. Kementerian Lingkungan Hidup dan Kehutanan. Sistem Informasi Pengelolaan Sampah Nasional: Komposisi Sampah Berdasarkan Jenis Sampah. 2024. Available online: https://sipsn.kemenlh.go.id/sipsn/public/data/komposisi (accessed on 01 September 2025).
3. BPS (Badan Pusat Statistik) Kota Tangerang Selatan. Kota Tangerang Selatan Dalam Angka 2025; BPS: Kota Tangerang Selatan, ID, 2025;
4. Tunggadewi, T.; Akbar, U.U. Analisis Willingness to Accept Dana Kompensasi Masyarakat Sekitar Tempat Pemrosesan Akhir (TPA) Cipeucang. J. Educ. Dev. 2023, 11, 444–449, doi:10.37081/ed.v11i2.4644.
5. Devaranti, S.; Khaerudin, M.R.; Lita, F.N.; Alamsyah, M.R.; Anggara, M.Y.; Kurniawan, I.A. Kebijakan Pengelolaan Sampah di Kabupaten Tangerang dan Tangerang Selatan. J. Pendidik. Sej. dan Ris. Sos. Hum. 2023, 3, 98–107.
6. Putri, A.D.; Oktavia, F.K. Evaluasi Kebijakan Dan Strategi Pengelolaan Sampah di Kota Tangerang Selatan. Syntax Idea 2023, 5, 1821–1836.
7. Kementerian Lingkungan Hidup dan Kehutanan, Republik Indonesia, Sistem Informasi Pengelolaan Sampah Nasional: Komposisi Sampah Berdasarkan Sumber Sampah di Kota Tangerang Selatan. 2024. Available online: https://sipsn.kemenlh.go.id/sipsn/public/data/sumber, (accessed on 01 September 2025).
8. Kementerian Lingkungan Hidup dan Kehutanan, Republik Indonesia, Sistem Informasi Pengelolaan Sampah Nasional: Komposisi Sampah Berdasarkan Jenis Sampah di Kota Tangerang Selatan. 2024. Available online: https://sipsn.kemenlh.go.id/sipsn/public/data/komposisi, (accessed on 01 September 2025).
9. Moh, Y.C.; Manaf, L.A. Overview of household solid waste recycling policy status and challenges in Malaysia. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 82, 50–61, doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2013.11.004.
10. Wan, C.; Shen, G.Q.; Choi, S. Differential public support for waste management policy: The case of Hong Kong. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 175, 477–488, doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.060
11. Botha, M.; Terblanche, S.E.; Luies, R. A decision support system for business development around decentralised waste utilisation in South Africa. Clean. Environ. Syst. 2022, 7, 100101, doi:10.1016/j.cesys.2022.100101.
12. Nurmaisyah, F.; Susilawati, S. Pengetahuan Masyarakat dalam Pengelolaan Sampah Rumah Tangga di Kecamatan Percut Sei Tuan. PubHealth J. Kesehat. Masy. 2022, 1, 91–96, doi:10.56211/pubhealth.v1i1.47.
13. Harun, H. Gambaran Pengetahuan dan Perilaku Masyarakat Dalam Proses Pemilahan Sampah Rumah Tangga di Desa Hegarmanah. J. Apl. Ipteks untuk Masy. 2017, 6, 86–88.
14. Hendrati, N. Persepsi Masyarakat Kota Surabaya Terhadap Bank Sampah Induk. J. Econ. Dev. Issues 2018, 1, 12–25, doi:10.33005/jedi.v1i2.16.
15. Sukerti, N.L.G.; Sudarma, I.M.; Pujaastawa, I.B.G. Perilaku Masyarakat Dalam Pengelolaan Sampah dan Faktor-Faktor yang Mempengaruhi di Kecamatan Denpasar Timur Kota Denpasar, Provinsi Bali. ECOTROPHIC J. Ilmu Lingkung. 2017, 11, 148–155, doi:10.24843/ejes.2017.v11.i02.p05.
16. Razali, F.; Daud, D.; Weng-Wai, C.; Jiram, W.R.A. Waste separation at source behaviour among Malaysian households: The Theory of Planned Behaviour with moral norm. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 271, 122025, doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122025.
17. Ajzen, I. The Theory of Planned Behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes 1991, 50, 179–211, doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/0749-5978(91)90020-T.
18. Hair, J.F.; Sarstedt, M.; Hopkins, L.; Kuppelwieser, V.G. Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM): An emerging tool in business research. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2014, 26, 106–121, doi:10.1108/EBR-10-2013-0128.
19. Yahya, A.; Affandy, A.; Narimawati, U. Pengembangan UMKM Melalui Pemanfaatan Model Layanan Fintech Syariah Ammana.id. is Best: Account. Inf. Syst. Inf. Technol. Bus. Enterp.2020; 5, 106–120, doi:10.34010/aisthebest.v5i2.3049.
20. Sarwono, J.; Narimawati, U. Membuat Skripsi, Tesis, dan Disertasi Dengan Partial Least Square; Penerbit Andi: Yogyakarta, ID, 2015;
21. Yandri, P. Residential Area and Income Inequality in Suburban Indonesia the important moment of changing in the pattern of development in Indonesia at least started in 2001. Indonesian Journal of Geography 2014, 45, 69–77.
22. Yandri, P. Conflicts and Segregation of Housing Cluster Communities and Its Surrounding. J. Kependud. Indones. 2015, 10, 75–88, doi:10.14203/jki.v10i2.68.
23. Yandri, P.; Priyarsono, D.; Fauzi, A.; Dharmawan, A.H. Pengembangan kriteria kawasan perumahan berkelanjutan di daerah suburban Indonesia.In Prosiding Seminar Nasional Seri 7, Yogyakarta, ID, 22 November 2017.
24. Yandri, P.; Priyarsono, D.S.; Fauzi, A.; Dharmawan, A.H. Formulating and Validating Sustainable Residential Area Indicators in Suburban Metropolitan Jakarta. Int. Rev. Spat. Plan. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 9, 82–102, doi:10.14246/irspsd.9.3_82.
25. Brotosusilo, A.; Handayani, D. Dataset on waste management behaviors of urban citizens in large cities of Indonesia. Data in Brief 2020, 32, 106053, doi:10.1016/j.dib.2020.106053.
26. Hariyanto, A. Implementasi Konsep Kebersihan Sebagian Daripada Iman di Kalangan Siswa MAN Lamongan. Kajian Moral dan Kewarganegaraan 2019, 7, 79–90.
27. Mujahidin, E.; Bahagia; Wibowo, R.; Dipa, L.Z.N.; Ningsih, S.R. Nilai Tradisi Bersih-Bersih di Lingkungan Sosial. J. Pendidik. Tambusai 2021, 5, 2194–2206
28. Cronk, L. Culture’s influence on behavior: Steps toward a theory. Evol. Behav. Sci. 2017, 11, 36–52, doi:10.1037/ebs0000069.
29. Yandri, P.; Budi, S.; Putri, I.A.P. Waste sadaqah: a new community-based waste management practice in Java, Indonesia. Sustain. Sci. Pract. Policy 2023, 19, 2212510, doi:10.1080/15487733.2023.2212510.
30. Yandri, P.; Budi, S.; Putri, I.A.P. Waste sadaqah: a new community-based waste management practice in Java, Indonesia. Sustain. Sci. Pract. Policy 2023, 19, 2212510, doi:10.1080/15487733.2023.2212510
31. Utomo, W.A.; Pasaribu, H.K.; Rambe, MF. Pengaruh Kepemimpinan dan Motivasi Kerja terhadap Kinerja Pegawai Dimediasi oleh Disiplin Kerja Pada Dinas Pencegah dan Pemadam Kebakaran Kota Medan. PIONIR J. Pendidik. 2021, 10, 125–140.
32. Arkorful, V.E.; Shuliang, Z.; Lugu, B.K. Investigating household waste separation behavior: the salience of an integrated norm activation model and the theory of planned behavior. Journal of Environmental Planning and Management 2022, 66, 2195–2221.
33. Xu, Z.; Shan, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, W. Extending the theory of planned behavior to predict public participation behavior in air pollution control: Beijing, China. Journal of Environmental Planning and Management 2019, 63, 669–688.
34. Tam, V.W.Y.; Tam, C.M. Waste reduction through incentives: A case study. Build. Res. Inf. 2008, 36, 37–43, doi:10.1080/09613210701417003.
Authors
Copyright (c) 2025 Pitri Yandri, Uki Masduki, Nur Aini, Siti Irma Suryani, Isnan Hari Mardika, Aldi Fathurrahman, Kardian Kardian

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).