Sustainable Wellness Tourism in Indonesia (Case Study on Health Tourism Development at Hanara Wellbeing Center Bandung)
Abstract
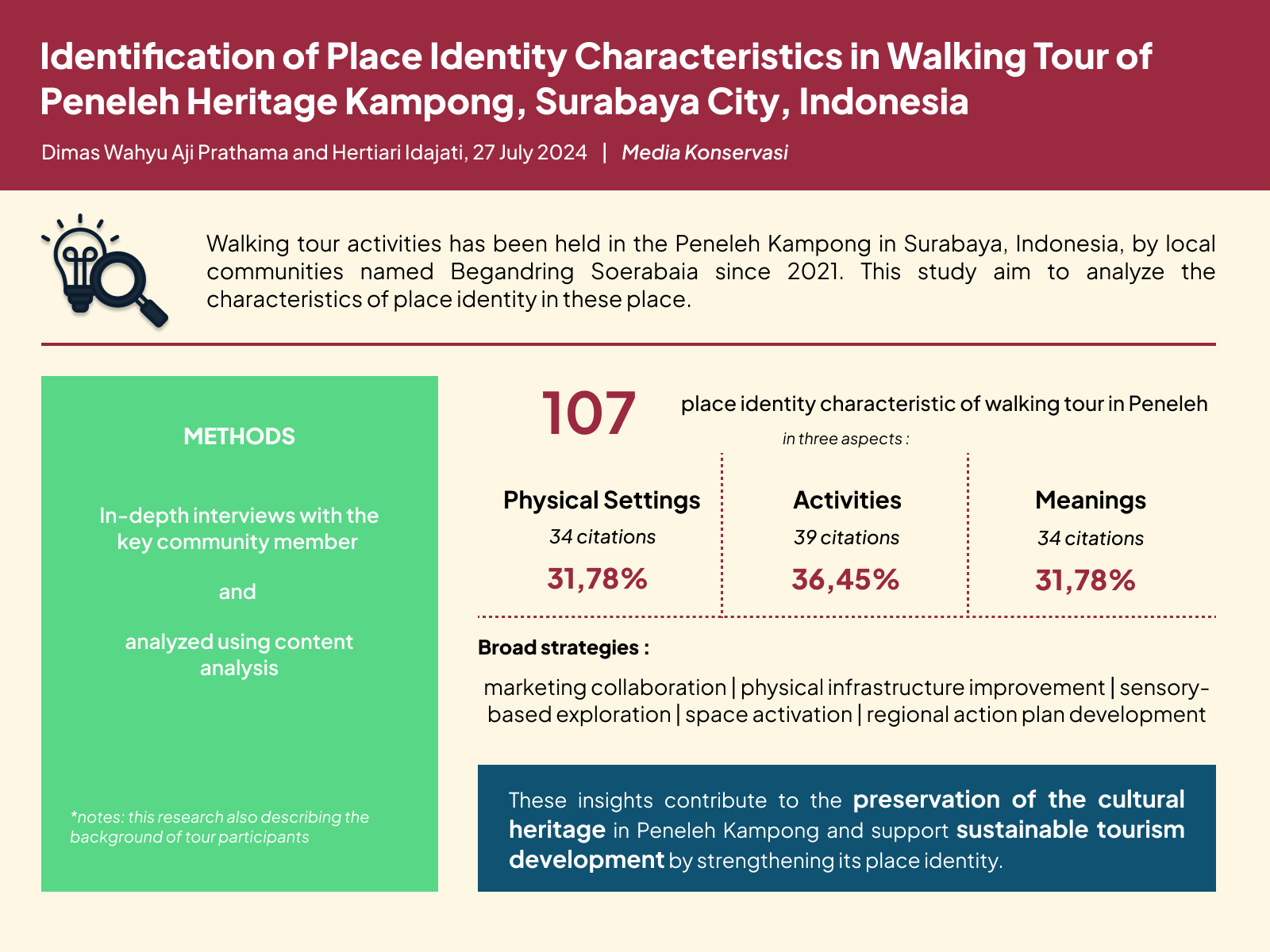
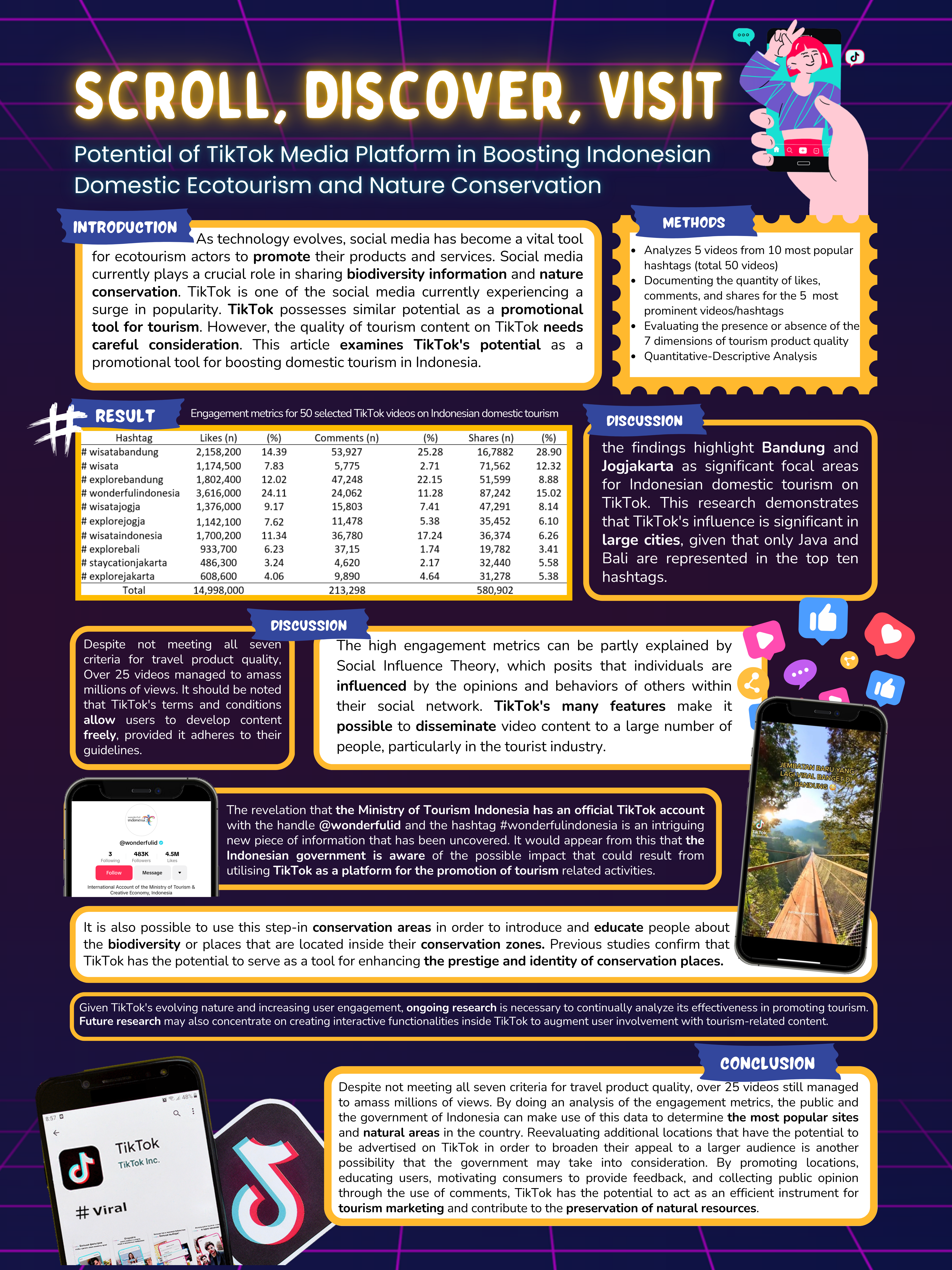
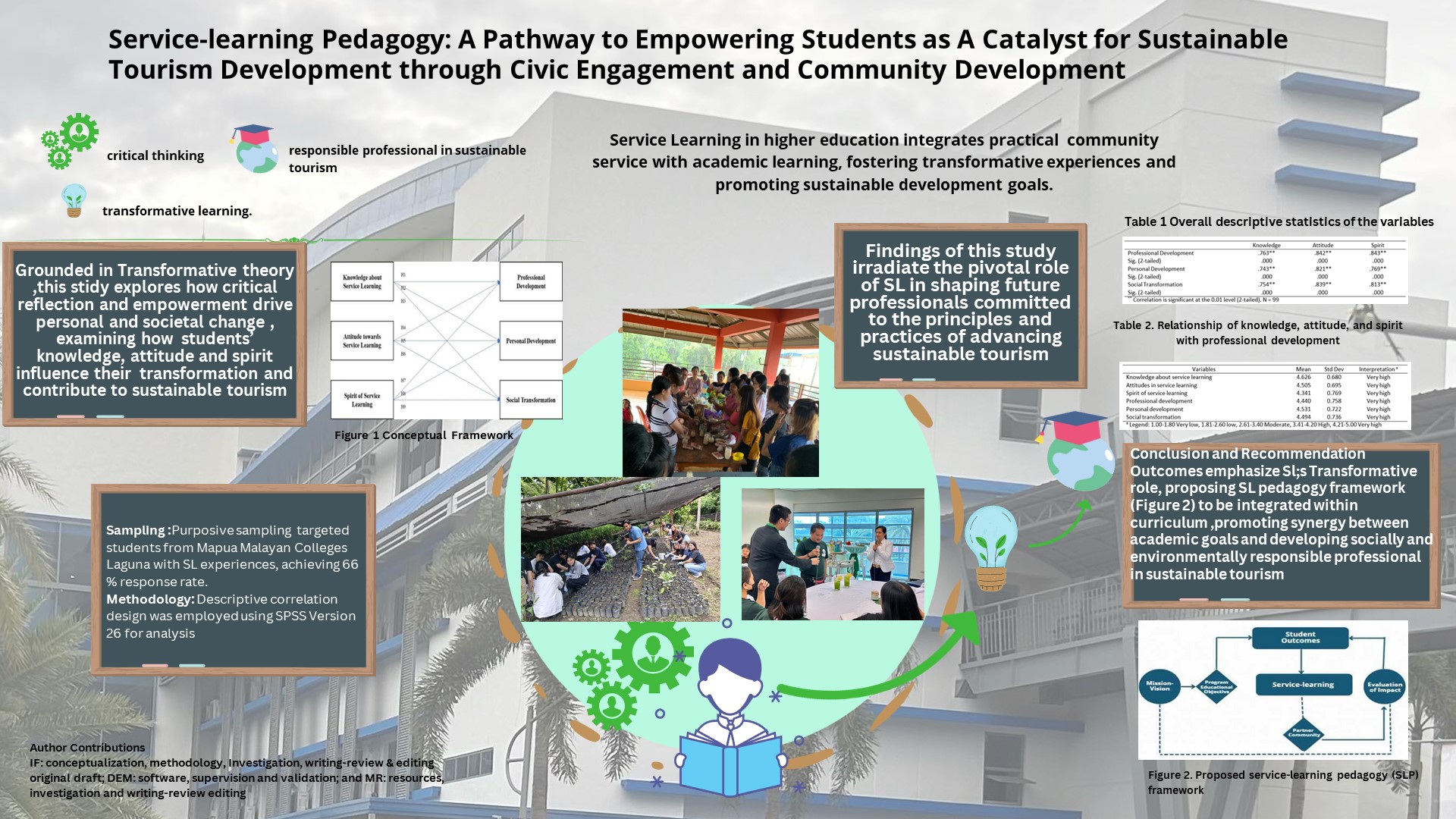
Wellness tourism is currently developing and starting to be recognized as an important aspect of tourism. Not only in Bali, Bandung is developing itself into a destination for foreign tourists for wellness tourism. Wellness tourism, which focuses on activities and experiences aimed at enhancing one's health and well-being, is intricately linked with sustainable tourism principles. This phenomenon is then studied using constructivist paradigms, qualitative methods, case study approaches, and social construction theory. Data collection techniques were participant observation for a year, interviews with 6 key informants and triangulation of 19 sources, literature study, and document study. The purpose of this study is to determine the development of wellness tourism in Bandung, Indonesia. The results showed that Bandung is an alternative to wellness tourism, because it was visited by patients from Malaysia, Canada, Singapore, Switzerland, the Philippines, Pakistan, Timor Leste and Australia. The uniqueness is: 1) Offering holistic health care; 2) Organizing complementary and alternative medicine under the supervision of doctors; 3) Spiritual healing-based care; 4) Teaching patients self-healing methods; 5) Not using chemical drugs; 6) Leaving the paternalistic model ;7) loyal patients are fostered in a community; and 8) using celebrities in promotions.
References
2. Pramono, J.; Dhyana, U.; Bali, P. Strategi Pengembangan Health and Wellnessdi Bali. Jurnal Manajemen, Strategi Bisnis dan Kewirausahaan, 2013, 7(1).
3. Utama, I. G. B. R.; Bagus, I. G. Health and Wellness Tourism: Types and Development Potential in Bali. International Journal of Social Science and Education Research Studies, 2021, 1-16.
4. Kristanto, T. B. A.; Putri, A. A. Pengembangan Masyarakat berbasis Aset sebagai Upaya Pemberdayaan Masyarakat melalui Sektor Wisata Kebugaran di Indonesia. Journal of Social Development Studies, 2021, 2(2), 43–54, doi: 10.22146/jsds.2272.
5. Kurniawati, F. Peran Healing Environment terhadap Proses Kesembuhan. Yogyakarta, 2007.
6. Putri, K. S. N. K.; Putri, I. A. K.; Suryaningsih, I. A. A. Journal of Hotel Service Management, 2022, 6, 125-131.
7. Yuwono, R.; Astuti, D. W. The potential for developing wellness hospitality tourism in Tawangmangu. Proc. (SIAR) of the 2021. Scientific Seminar on Architecture, 2021, 282-292.
8. Utami, Y. S.; Andriani, A. D.; Chotimah, D. H. Cuba Village Program Implementation of Health Communication. Garut University Communication Journal: Thought and Research Results, 2021, 7(2), 687-698.
9. Prasojo, M. N. B. Konstruksi Sosial Masyarakat terhadap Alam Gunung Merapi: Studi Kualitatif tentang Kearifan Lokal yang Berkembang di Desa Tlogolele Kecamatan Selo Kabupaten Boyolali. Jurnal Analisa Sosiologi, 2015, 4(2), 31-46.
10. Muta’afi. Konstruksi Sosial Masyarakat terhadap Penderita. Paradigma, 2015, 3(3).
11. Kuswarno, E. Etnografi Komunikasi, Suatu Pengantar dan Contoh Penelitiannya, Bandung, Widya Padjadjaran, 2008.
12. Alfanani, T.S. Konstruksi Sosial Komunitas Pesantren Mengenai Isu Radikalisme (Studi Kasus pada Pesantren Salaf dan Modern di Kota Malang). Sosiologi Agama: Jurnal Ilmiah Sosiologi Agama dan Perubahan Sosial, 2016, 10(2).
13. Sutarya, I. G. Daya Tarik Yoga dalam Pariwisata Wellness. Jurnal Pariwisata Budaya, 2016, I(1), 35–40. https://doi.org/10.1109/ciced.2018.8592188.
14. Andriani, A.D. Word of Mouth Communication dalam Memperkenalkan Program Self Healing (Studi Kasus pada Klinik Hanara Well Being Center, Bandung. Journal of Social and Political Sciences, 2019, 2(1) 33-53.
15. Andriani, A. D. Komunikasi Terapeutik Terapi Self Healing pada Pasien PTM Prioritas. J. Commun. Stud.,2022, 6 (2), 233-250.
16. Andriani, A.D.; Mulyana, D.; Dida, S.; Wahyudin, U. The Role of Healing Environment in Reducing the Stress of Patients with Non-Communicable Disease. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med., 2021, 12, 300–306, doi: 10.4103/jnsbm.JNSBM_12_3_7.
17. Andriani, A.D. Holistic Medicine in Health Communication Approach. Int. Conf. on Health Science, Green Economics, Educational Review and Technology, 2021, 3, 201-212.
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Media Konservasi is an open access journal, meaning that all content is freely available without charge to the user or their institution. Users are allowed to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts of the articles in this journal without needing to request prior permission from the publisher or the author.
All articles published by Media Konservasi are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. This allows for unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided proper credit is given to the original authors.
Authors submitting manuscripts should understand and agree that the copyright of published manuscripts is retained by the authors. Copyright encompasses the exclusive rights of authors to reproduce, distribute, and sell any part of the journal articles in all forms and media. Reproduction of any part of this journal, its storage in databases, and its transmission by any form or media is allowed without written permission from Media Konservasi.