Ecology of Hornbill Food Trees at Bukit Barisan Selatan National Park
Abstract
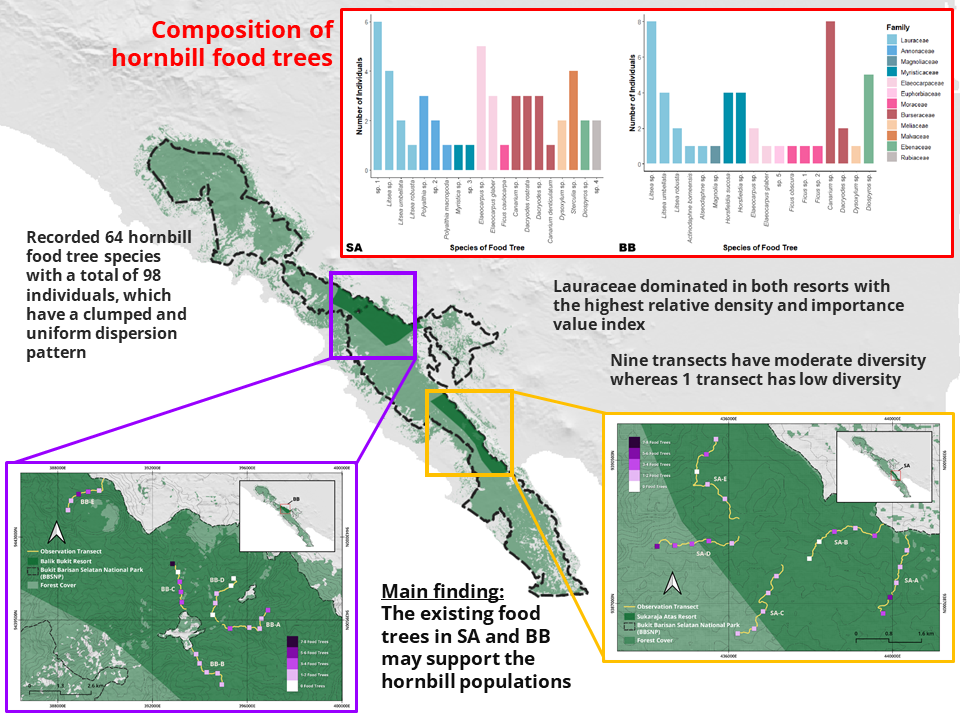
Hornbills play an important role in maintaining tree gene flow among fragmented populations in forests. But hornbill populations in Asia have been declining, mainly due to loss of forest cover and poaching. The presence of hornbills in a forest is highly dependent on environmental factors such as the condition of food trees in their habitat. The purpose of this study was to determine the spatial distribution, dispersion patterns, density, importance value index, and diversity of hornbill food trees at Sukaraja Atas Resort (SA) and Balik Bukit Resort (BB) of Bukit Barisan Selatan National Park (BBSNP). We investigated a total of 10 transects (50 survey plots) for both SA and BB by collecting data on all types of hornbill food trees with a minimum diameter of 10 cm at breast height (DBH). We recorded 64 hornbill food tree species with a total of 98 individuals, which have a clumped and uniform dispersion pattern. This study showed that Lauraceae dominated in both resorts with the highest relative density and importance value index. The results of the diversity index show that 9 transects have moderate diversity whereas 1 transect has low diversity; there was no significant difference between SA and BB. It can be concluded that the existing food trees in SA and BB may support the hornbill populations.
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Media Konservasi is an open access journal, meaning that all content is freely available without charge to the user or their institution. Users are allowed to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts of the articles in this journal without needing to request prior permission from the publisher or the author.
All articles published by Media Konservasi are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. This allows for unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided proper credit is given to the original authors.
Authors submitting manuscripts should understand and agree that the copyright of published manuscripts is retained by the authors. Copyright encompasses the exclusive rights of authors to reproduce, distribute, and sell any part of the journal articles in all forms and media. Reproduction of any part of this journal, its storage in databases, and its transmission by any form or media is allowed without written permission from Media Konservasi.