Potential for Developing Access to Safe Drinking Water in the Highlands Area (Case Study: Bogor City, Indonesia)
Abstract
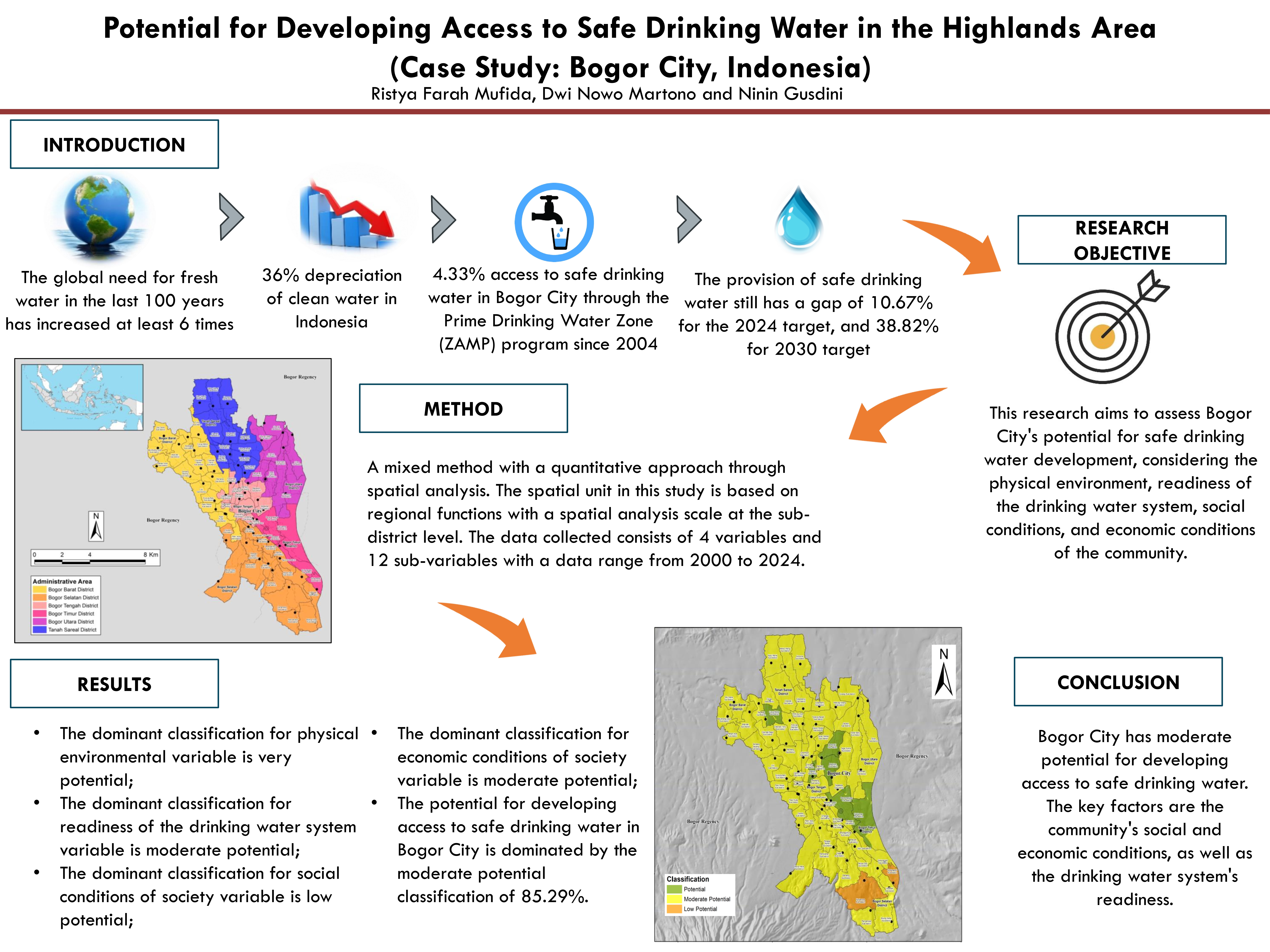
The need for water in Indonesia is not directly proportional to its availability. This challenge is not limited to rural areas but also affects urban areas like Bogor City. Since 2004, Regional drinking water company of Bogor City has been classified as healthy and is a pilot city for the prime drinking water zone program alongside two other Indonesian cities. This research aims to assess Bogor City's potential for safe drinking water development, considering the physical environment, readiness of the drinking water system, social conditions, and economic conditions of the community. The methodology used is mixed with a quantitative approach via spatial analysis. The physical environment variable yielded 4 classifications: high potential, potential, moderate potential, and low potential. The very potential classification was dominant in 45 sub-districts. The drinking water system readiness had 4 classifications: potential, moderate potential, low potential, and no potential, with the moderate potential dominating in 51 sub-districts. The community social condition had 4 classifications: potential, moderate potential, low potential, and no potential, with the low potential dominating in 36 sub-districts. The community economic condition variable resulted in 4 classifications. Moderate potential dominates in 29 sub-districts. Bogor City has moderate potential for developing access to safe drinking water. The key factors for this classification are the community's social and economic conditions, as well as the drinking water system's readiness.
Full text article
References
Susana, T. Air Sebagai Sumber Kehidupan. Oseana 2003, 28, 17–25.
UNESCO The United Nations World Water Development Report 2021: VALUING WATER Facts and Figures; 2021;
Phan, T.D.; Bertone, E.; Stewart, R.A. Critical Review of System Dynamics Modelling Applications for Water Resources Planning and Management. Clean. Environ. Syst. 2021, 2.
Oki, T.; Kanae, S. Global Hydrological Cycles and World Water Resources. Science (80-. ). 2006, 313, 1068–1072.
Wada, Y.; Flörke, M.; Hanasaki, N.; Eisner, S.; Fischer, G.; Tramberend, S.; Satoh, Y.; Van Vliet, M.T.H.; Yillia, P.; Ringler, C.; et al. Modeling Global Water Use for the 21st Century: Water Futures and Solutions (WFaS) Initiative and Its Approaches. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 175–222, doi:10.5194/gmdd-8-6417-2015.
Kementerian Perencanaan Pembangunan Nasional/ Badan Perencanaan Pembangunan Nasional (Bappenas) Pilar Pembangunan Lingkungan; Jakarta, 2020;
Samekto, C.; Winata, E.S. Potensi Sumber Daya Air Di Indonesia. Semin. Nas. Apl. Teknol. Penyediaan Air Bersih untuk Kabupaten/Kota di Indones. 2004, 1–20.
Radhika; Firmansyah, R.; Hatmoko, W.; Sumber Daya Air, P.; Pekerjaan Umum dan Perumahan Rakyat, K.; Ir Juanda, J.H. PERHITUNGAN KETERSEDIAAN AIR PERMUKAAN DI INDONESIA BERDASARKAN DATA SATELIT COMPUTATION OF SURFACE WATER AVAILABILITY IN INDONESIA BASED ON SATELLITE DATA. J. Sumber Daya Air 2017, 13, 115–130.
Badan Pusat Statistik Statistik Indonesia Dalam Infografis, 2017; 2017;
Abidin, H.Z.; Andreas, H.; Gumilar, I.; Brinkman, J.J. Study on the Risk and Impacts of Land Subsidence in Jakarta. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the International Association of Hydrological Sciences; Copernicus GmbH, November 12 2015; Vol. 372, pp. 115–120.
Prayoga, R.; Nastiti, A.; Schindler, S.; Kusumah, S.W.D.; Sutadian, A.D.; Sundana, E.J.; Simatupang, E.; Wibowo, A.; Budiwantoro, B.; Sedighi, M. Perceptions of Drinking Water Service of the ‘off-Grid’ Community in Cimahi, Indonesia. Water (Switzerland) 2021, 13, doi:10.3390/w13101398.
SKAM-RT Studi Kualitas Air Minum Rumah Tangga Di Indonesia; 2020;
Gleick, P.H.; Cooley, H.S. Energy Implications of Bottled Water. Environ. Res. Lett. 2009, 4, doi:10.1088/1748-9326/4/1/014009.
Turrini, T.; Knop, E. A Landscape Ecology Approach Identifies Important Drivers of Urban Biodiversity. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 1652–1667, doi:10.1111/gcb.12825.
Boretti, A.; Rosa, L. Reassessing the Projections of the World Water Development Report. npj Clean Water 2019, 2, doi:10.1038/s41545-019-0039-9.
Chatterjee, C.; Triplett, R.; Johnson, C.K.; Ahmed, P. Willingness to Pay for Safe Drinking Water: A Contingent Valuation Study in Jacksonville, FL. J. Environ. Manage. 2017, 203, 413–421, doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.08.008.
Bach, C.; Dauchy, X.; Chagnon, M.C.; Etienne, S. Chemical Compounds and Toxicological Assessments of Drinking Water Stored in Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Bottles: A Source of Controversy Reviewed. Water Res. 2012, 46, 571–583, doi:10.1016/j.watres.2011.11.062.
Wardhana, Y.M.A. Policy Model for Sustainable Drinking Water Supply System. J. Infrastruct. Policy Manag. 2018, 1.
Bappenas Rencana Pembangunan Jangka Menengah Nasional 2020-2024; 2019;
Kementerian Perencanaan Pembangunan Nasional/ Badan Perencanaan Pembangunan Nasional Peta Jalan Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Di Indonesia; 2017;
Gumilar, A.. Kajian Strategi Pengembangan Zona Air Minum Prima (Zamp)Pada Kelompok Pelanggan Rumah Tangga Di Kota Bogor(Studi Kasus: Eksisting Zamp Di Kecamatan Bogor Selatan Dan Timur). J. Pembang. Wil. Kota 2015, 11.
Kementerian Pekerjaan Umum dan Perumahan Rakyat Kinerja BUMD Air Minum 2021; 2021;
Dinas Lingkungan Hidup Kota Bogor Status Lingkungan Hidup Daerah (SLHD) Kota Bogor-Provinsi Jawa Barat; 2015;
Farley, M.; Wyeth, G.; Bin Md. Ghazali, Z.; Istandar, A.; Singh, S. Buku Pegangan Tentang Air Tak Berekening (NRW) Untuk Manajer: Panduan Untuk Memahami Kehilangan Air; 2008;
Natalia, M.B.; Mardiyono; Said, A. IMPLEMENTASI PROGRAM ZONA AIR MINUM PRIMA (ZAMP) UNTUK MEMENUHI KEBUTUHAN AIR MINUM MASYARAKAT (Studi Pada PDAM Kota Malang). J. Adm. Publik 2014, 2, 11–15.
Sima, L.C.; Desai, M.M.; McCarty, K.M.; Elimelech, M. Relationship between Use of Water from Community-Scale Water Treatment Refill Kiosks and Childhood Diarrhea in Jakarta. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2012, 87, 979–984, doi:10.4269/ajtmh.2012.12-0224.
Gubernur Jawa Barat Keputusan Gubernur Jawa Barat Upah Minumum Kabupaten/Kota Di Daerah Provinsi Jawa Barat Tahun 2024. 2023.
BPS Kota Bogor Kota Bogor Dalam Angka 2023; 2023;
Isaac, S.; Michael, W.B. Handbook in Research and Evaluation: A Collection of Principles, Methods, and Strategies Useful in the Planning, Design, and Evaluation of Studies in Education and the Behavioral Sciences, 3rd Ed.; EdITS Publishers: San Diego, CA, US, 1995; ISBN 0-912736-25-9 (Paperback).
Terfrüchte, T.; Frank, S. Delineating and Typifying Urban Neighbourhoods: A Mixed-Methods Approach. Metrop. Res. Methods Approaches 2022, 343–365, doi:10.1515/9783839463109-020.
Lahan, D.J.R. dan R. Keputusan Direktur Jenderal Reboisasi Dan Rehabilitasi Lahan (Ditjen RRL) Nomor 041/Kpts/V/1998 Tanggal 21 April 1998 Tentang Pedoman Penyusunan Rencana Tehnik Lapangan Rehabilitasi Lahan Dan Konservasi Tanah Daerah Aliran Sungai; Jakarta, 1998;
Shi, K.; Yu, B.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yin, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, L.; Wu, J. Evaluating the Ability of NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Data to Estimate the Gross Domestic Product and the Electric Power Consumption of China at Multiple Scales: A Comparison with DMSP-OLS Data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1705–1724, doi:10.3390/rs6021705.
Yu, B.; Shi, K.; Hu, Y.; Huang, C.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. Poverty Evaluation Using NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Composite Data at the County Level in China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 1217–1229, doi:10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2399416.
Ranjith, S.; Jennifer, W. Codification Challenges for Data Science in Construction. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2020, 146, 4020072, doi:10.1061/(ASCE)CO.1943-7862.0001846.
Rêgo, A. da S.; Radovanovic, C.A.T.; Haddad, M. do C.F.L.; Santos, J.L.G. dos; Carreira, L.; Salci, M.A.; Andrade, L. de; Büscher, A. USE OF GROUNDED THEORY IN THE EXTRACTION, CODING AND ANALYSIS OF DATA IN LITERATURE META-ANALYSES. Texto Context. - Enferm. 2023, 32.
Rukmana, C.S.; Armono, H.D.; Wahyudi Studi Potensi Obyek Wisata Pantai Di Kabupaten Sampang. Tek. Pomits 2013, 2, 52–55.
Noperissa, V.; Waspodo, R.S.B. Analisis Kebutuhan Dan Ketersediaan Air Domestik Menggunakan Metode Regresi Di Kota Bogor. J. Tek. Sipil dan Lingkung. 2018, 3, 121–132, doi:10.29244/jsil.3.3.121-132.
Simonovic, S.P.; Fahmy, H. A New Modeling Approach for Water Resources Policy Analysis. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 295–304, doi:10.1029/1998WR900023.
Sanchez, A.S.; Oliveira-Esquerre, K.P.; Nogueira, I.B.; de Jong, P.; Filho, A.A. Water Loss Management Through Smart Water Systems. Springer Nat. Switz. AG 2020, 17, 233–266.
Asmara, G. Peluang Dan Tantangan Pengendalian Kehilangan Air Berbasis Internet of Things (Iot) : Studi Pustaka the Opportunities and Challenges of Water Losses Control Based on Internet of Things (Iot) : Literature Review. Jukung J. Tek. Lingkung. 2021, 7, 188–196.
Purwanto, E.W. Pembangunan Akses Air Bersih Pasca Krisis Covid-19. Indones. J. Dev. Plan. 2020, IV.
Herlambang, A.; Martono, D.H. Teknologi Pengolahan Sampah Dan Air Limbah. J. Air Indones. 2018, 4, 146–160, doi:10.29122/jai.v4i2.2422.
Arisandi, P.; Jindrich; Yuyun; Joseph; Lee; Bjorn Sampah Plastik Meracuni Rantai Makanan Indonesia; 2019;
Pierce, G. Why Is Basic Service Access Worse in Slums? A Synthesis of Obstacles. Dev. Pract. 2017, 27, 288–300, doi:10.1080/09614524.2017.1291582.
WHO; Unicef Air, Sanitasi Dan Pengelolaan Limbah Yang Tepat Dalam Penanganan Wabah COVID-19. Pedoman Sementara WHO dan UNICEF 19 Maret 2020 2020, 2–4.
Hofmann, P. Toward Equitable Urban Water Supply and Sanitation in Dar Es Salaam: The Dialectic Relationship between Policy-Driven and Everyday Practices. Util. Policy 2022, 78, doi:10.1016/j.jup.2022.101395.
Negeri, P.M.D. Peraturan Menteri Dalam Negeri Republik Indonesia Nomor 21 Tahun 2020 Tentang Perubahan Atas Peraturan Menteri Dalam Negeri Nomor 71 Tahun 2016 Tentang Perhitungan Dan Penetapan Tarif Air Minum; 2020;
Liu, Z.; Liu, W. Spatial–Temporal Relationship between Water Resources and Economic Development in Rural China from a Poverty Perspective. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, doi:10.3390/ijerph18041540.
Wesli, W.; Fasdarsyah, F.; Kurniawan, I.; Yusuf, K.; Akbar, S.J.; Maizuar, M.; Arfiandi, J. Perencanaan Jaringan Perpipaan Air Minum Menggunakan Aplikasi Watercad V8-I. Teras J. J. Tek. Sipil 2021, 11, 413, doi:10.29103/tj.v11i2.554.
Riduan, R.; Firmansyah, M.; Fadhilah, S. Evaluasi Tekanan Jaringan Distribusi Zona Air Minum Prima (Zamp) Pdam Intan Banjar Menggunakan Epanet 2.0. Jukung (Jurnal Tek. Lingkungan) 2017, 3, 12–20, doi:10.20527/jukung.v3i1.3195.
Afrianita, R.; Komala, P.S.; Andriani, Y. Kajian Kadar Sisa Klor Di Jaringan Distribusi Penyediaan Air Minum Rayon 8 PDAM Kota Padang. Semin. Nas. Sains dan Teknol. Lingkung. II 2016, 144–151.
Fontana, M.G. Corrosion Engineering; 3rd Edition. McGraw-Hill: New York, 1986;
Alihar, F. Penduduk Dan Akses Air Bersih Di…| Fadjri Alihar Penduduk dan Akses Air Bersih di Kota Semarang (Population and Access to Clean Water in Semarang City). J. Kependud. Indones. | 2018, 13, 67–76.
Maasing, D.I.K.; Tuminting, K.; Manado, K. Analisis Kebutuhan Prasarana Dasar Permukiman. Sabua 2014, 6, 199–206.
Authors
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).