Macro-Nutrient Prediction of Paddy Field Soil Using Artificial Neural Network and NIR Spectroscopy
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.19028/jtep.012.2.242-258Keywords:
Bahasa IndonesiaAbstract
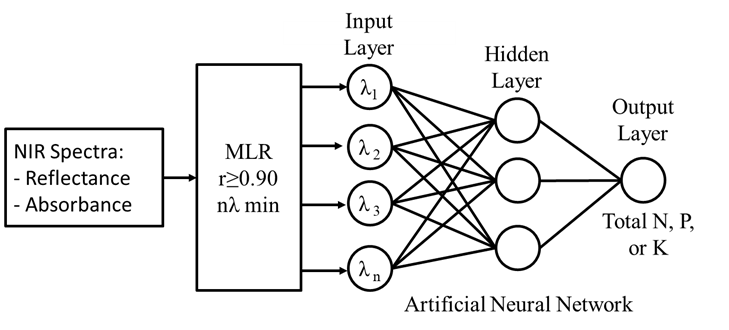
Understanding soil fertility, influenced by macronutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, is essential for adaptive agriculture implementation based on various soil conditions. Near-infrared spectroscopy technology provides non-destructive, rapid soil property measurements without chemicals, applicable both in-field and in-laboratory. However, the wide NIR spectrum range and neural network complexities can hinder Artificial Neural Network (ANN) training and inference, leading to time and resource inefficiency, especially without sophisticated computing devices. This study examines data reduction methods to enhance ANN performance in predicting soil macronutrients using NIR spectra. Multiple Linear Regression (MLR) and Principal Component Analysis (PCA) were applied to select wavelengths from the 1000–2500 nm for ANN input, comparing their performance. About 237 NIR reflectance data from paddy soil were transformed into absorbance data. MLR used forward selection to identify wavelengths with correlations higher than 0.9, while PCA selected wavelengths corresponding to the loading factor peaks for each principal component. These selected wavelengths served as inputs for the ANN model. The ANN’s performance was assessed using correlation and determination coefficients, RMSE, RPD, and model consistency. For nitrogen, the PCA+ANN model with reflectance spectra performed better (RPD 2.4-4.8) than the MLR+ANN model (RPD 2.2-2.6) using fewer wavelengths (5-9 for PCA+ANN vs. 9-12 for MLR+ANN). For phosphorus estimation, the PCA+ANN model also excelled (RPD 2.3-7.0 vs. 2.3-2.4) with fewer wavelengths (4-7 vs. 7). For potassium estimation, the PCA+ANN model showed superior performance (RPD 4.3-9.5 vs. 4.2-4.4), using the same number of wavelengths (4-8 vs. 4-6).
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Authors submitting manuscripts should understand and agree that copyright of manuscripts of the article shall be assigned/transferred to Jurnal Keteknikan Pertanian. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License (CC BY-SA) where Authors and Readers can copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format, as well as remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, but they must give appropriate credit (cite to the article or content), provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. If you remix, transform, or build upon the material, you must distribute your contributions under the same license as the original.





















