Utilizing Demographic, Ethnic, and Human Emotional Variables to Enhance Compassion Feeling: Basis for Slow Lorises Conservation Extension Media Development
Abstract
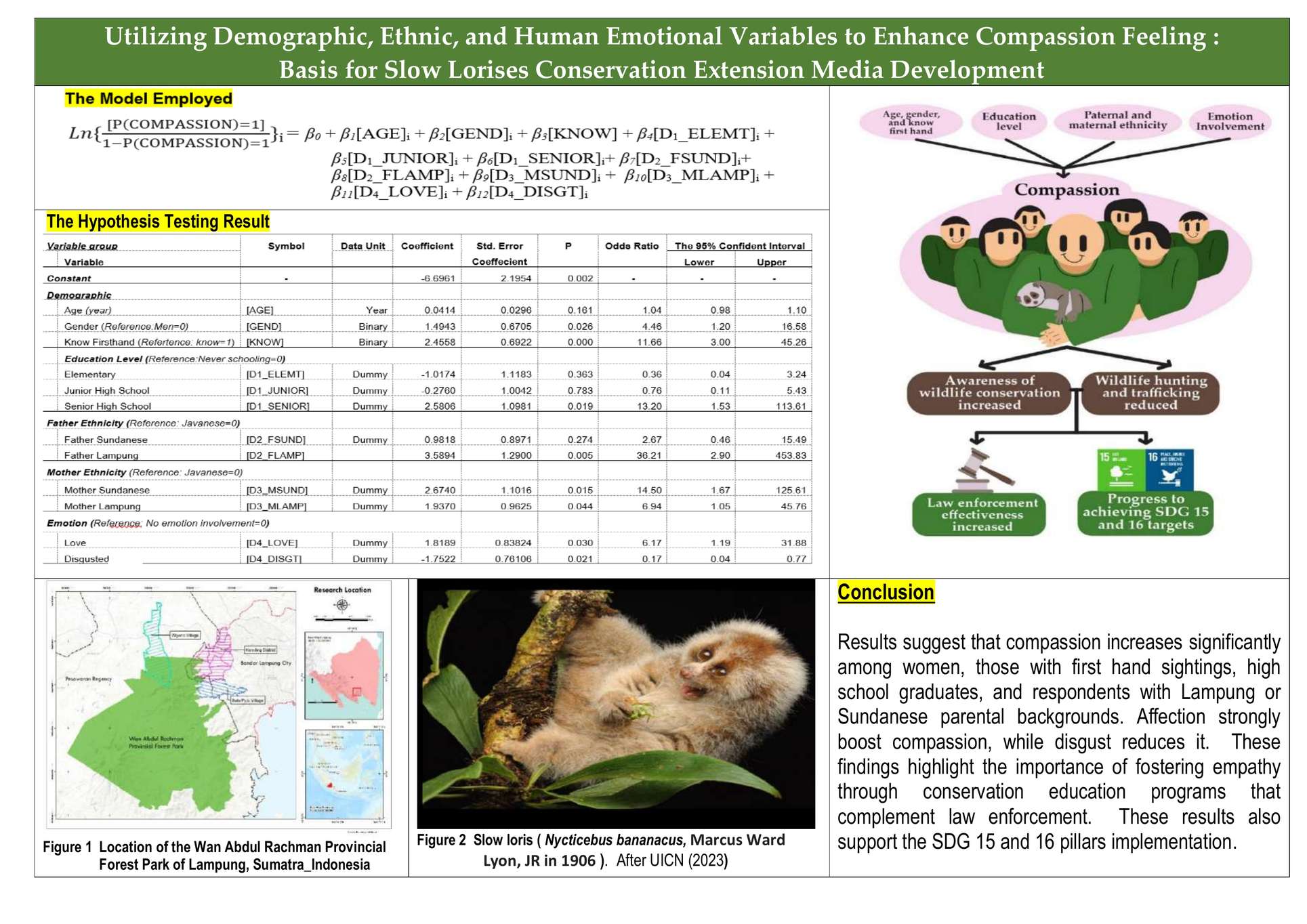
Slow lorises, listed as endanger under CITES Appendex I, are increasingly found outside forest habitate, including the buffer zone of Wan Abdul Rachman Grand Forest Park (Tahura WAR) in Lampung Province. While this coexistence support ex-situ conservation, it also raises risks of illegal hunting and trafficking. This study investigates how demographics, education, ethnicity, and emotion influence compassion (COMP) toward slow lorises. A log-linear model was applied at a 95% confidence level. The response variable [COMP] was scored as 1 if respondents expressed compassion, and 0 otherwise. Explanatory variables included esmotions (affection, neutral, disgust), prior direct sightings, education level, and ethnic background. Data were collected through door-to-door survey of 150 respondents across three villages in the Tahura WAR buffer zone during October–November 2023. Each respondent was shown a 20 cm × 30 cm photograph of slow loris before answering. Results suggest that compassion increases significantly among women, those with fisthand sightings, high school gradustes, and respondents with Lampung or Sundanese parental backgrounds. Affection strongly boost COMP, while digust reduces it. These findings highlight the importance of fostering empathy through conservation education programs that complement law enforcement. These results also support the SDG 15 and 16 pillars implementation.
Full text article
References
2.Bakri, S., Apriliani, A.P., Kaskoyo, H., & Wulandari. (2024). Are the physical and social capitals still critical factors in enhancing the sluggish productivity of coffee agroforestry?: The evidence of endogenous growth role at Batutegi Forest Management Unit. Jurnal Manajemen Hutan Tropika, 30(2):284-294, DOI: 10.7226/jtfm.30.2.284.
3.Bakri S., Karomani K., & Ashaf, A. F. (2021). The role of extension participation on risk-taking behavior of local elites and the coffee agroforestry farmer‘s income: A case study at social forest community on Batutegi Forest Management Unit, Lampung. IOP Conf. Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 739 (2021) 012006 IOP Publishing. doi:10.1088/1755-1315/739/1/012006.
4.Blair, M.E., Cao, G.T.H., López-Nandam, E.H., Veronese-Paniagua, D.A., Birchette, M.G., Kenyon, M., Md-Zain, B.M., Munds, R.A., Nekaris, K.A., Nijman, V., Roos, C., Thach, H.M., Sterling, E.J., & Le, M.D. (2024). Molecular phylogenetic relationships and unveiling novel genetic diversity among slow and pygmy lorises, including the resurrection of Xanthonycticebus intermedius. Genes, 14 (643):1-26. https://doi.org/ 10.3390/genes14030643.
5.Bevir, M., & Stueber, K. (2011). Empathy, rationality, and explanation. Journal of Philosophy History, 5(2):147-162. DOI: 10.1163/187226311X582293.
6.Beadle, J.N., & de la Vega, C.E. (2019). Impact of aging on empathy: Review of psychological and neural mechanisms. Frontier in Psychiatry, 10:331. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00331.
7.Beausoleil, N.J. (2020). I am a compassionate conservation welfare scientist: Considering the theoretical and practical differences between compassionate conservation and conservation welfare. Animals, 10:1-20. doi:10.3390/ani10020257.
8.Buya, S., Tongkumchum, P., & Owusu, B.E. (2020). Modeling of land-use change in Thailand using binary logistic regression and multinomial logistic regression. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 13:437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05451-2.
9.Castillo-Huitron, NM, Naranjo EJ, Santos-Fita D, Estrada-Lugo, E. 2020. The importance of human emotions for wildlife conservation. Frontier in Psychology, 31:1177-1288. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01277.
10.Choudhury, A.S., Choudhury, P., & Gassah, R. (2022). Habitat suitability modeling for the endangered Bengal slow loris (Nycticebus bengalensis) in the Indo-Chinese subregion of India: A case study from Southern Assam (India). Primates 63: 173–184 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10329-021-00967-x.
11.Critchlow, R., Plumptre, A. J., Alidria, B., Nsubuga, M., Driciru, M., Rwetsiba, A., Wanyama, F., & Beale, C.M. (2017). Improving law-enforcement effectiveness and efficiency in protected areas using ranger-collected monitoring data. Conservation Letters, 10(5):572–580, doi: 10.1111/conl.12288.
12.Dalton, E.M. (2017). Beyond universal learning design: Guiding principles to reduce barriers to digital and media literacy competence. Journal of Media Literacy Education, 9 (2):17-29, https://doi.org/10.23860/JMLE-2019-09-02-02.
13.Deniz, F., Anwar, O., Elizalde, N., Huth, A.G., & Gallant, J.L. (2019). The representation of semantic information across human cerebral cortex during listening versus reading is invariant to stimulus modality. Journal of Neuroscience, 39 (39):722-7736 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0675-19.2019.
14.de Oliveira, J.V.D., Silva, M.X.G.D., Borges, A.K.M., Souto, W.M.S., Lopes, S.D.F., Trovão, D.M.D.B.M., Barboza, R.R.D., & Alves RRN. (2020). Fauna and conservation in the context of formal education: A study of urban and rural students in the semi-arid region of Brazil. Journal of Ethnobiology and Ethnomedicine,7 (16):-15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13002-020-00374-4
15.Deschênes, L.C., Goulet, M.H., & Pariseau-Legault, P. (2022). Factors associated with perceived coercion in adults receiving psychiatric care: A scoping review protocol. BMJ Open, 12:e065393. doi:10.1136/ bmjopen-2022-065393.
16.Dushkova, D., & Ivlieva, O. (2024). Empowering communities to act for a change: A review of the community empowerment programs towards sustainability and resilience. Sustainability, 16, 8700. https:// doi.org/10.3390/su16198700.
17.Engels, J.M.M., & Ebert, AW. (2020). A critical review of the current global ex-situ conservation system for plant agrobiodiversity. History of the development of the global system in the context of the political/legal framework and its major conservation components. Plants 10, 1557. https:// doi.org/10.3390/plants10081557.
18. Erickson, E. H. 1963. Childhood and Society (2nd ed.) Harmondsworth: Penguin Books.
19.Fiorenzato E, Bisiacchi P, Cona G. (2024). Gender differences in the effects of emotion induction on intertemporal decision-making. PLoS ONE 19(3): e0299591. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0299591.
20.Gebregziabher, D., & Soltani, A. (2019). Exclosures in people‘s minds: Perceptions and attitudes in the Tigray region, Ethiopia. Forest Policy and Economics, 101:1-14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forpol.2019.01.012.
21.Feng, G.C., Yu, Y.L.Z., & Wen, J.W. (2023). Effects of rhetorical devices on audience responses with online videos: An augmented elaboration likelihood model. PLoS ONE, 18(3): e0282663. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0282663.
22.Gilleard, C. (2020). The final stage of human development? Erikson’s view of integrity and old age. International Journal of Ageing and Later Life, 14(2): 139–162. Doi: 10.3384/ijal.1652-8670.1471.
23.Gudicha, D.W., Schmittmann, V.D., & Vermunt, J.K. (2017). Statistical power of likelihood ratio and Wald Tests in latent class models with covariates. Research Behavior, 49:1824–1837. DOI 10.3758/s13428-016-0825y.
24.Hanci, H. (2022). Investigation of high school students' visual literacy levels. International Journal of Research in Education and Science, 8(3): 611-625. https://doi.org/10.46328/ijres.2980.
25.Harryadi, A.F. (2020). Understanding different ethnic cultures in Indonesia and how they do business. https://brightindonesia.net.
26.Hochberg, Z., & Konner, M. (2020). Emerging adulthood is a pre-adult life-history stage. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 10:918. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00918
27.Hong, H.J., Kim, C.K., Lee, H.W., & Lee, W.K. (2021). Conservation, restoration, and sustainable use of biodiversity based on habitat quality monitoring: A case study on Jeju Island, South Korea (1989–2019). Land, 10:774. https://doi.org/ 10.3390/land10080774.
28.Holden, M.H., Biggs, D., Brink, H., Bal, P., Jonathan Rhodes, J., & McDonald-Madden, E. (2019). Increase anti-poaching law enforcement or reduce demand for wildlife products? A framework to guide strategic conservation investments. Conservation Letters, 12 (3);1-9. https://doi.org/10.1111/conl.12618.
29.IUCN. (2023). Indonesia Has 189 Critically Endangered Fauna, 26 Species are Mammals. Report 2023.
30.Jacobs, R., & Barnard, A. (2022). Authenticity as best-self: The experiences of women in law enforcement. Frontier in Psychology, 13:861942. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.861942.
31.Kansky, R., & Maassarani, T. (2022). Teaching nonviolent communication to increase empathy between people and toward wildlife to promote human-wildlife coexistence. Conservation Letters. 2022;15:e12862. 1 of 11 https://doi.org/10.1111/conl.12862.
32.Kim, H.B., Choi, S., Kim, B., & Pop-Eleches, C. (2018). The role of education interventions in improving economic rationality. Science, 362(6410): 83-86, DOI: 10.1126/science.aar6987.
33.Kimmig, A.C.S., Wildgruber, D., Wendel, S.M.U., Poroma, I.S., & Derent, B. (2021). Friend vs foe: Cognitive and affective empathy in women with different hormonal states. Neuroendocrine Science, 15: 1-12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2021.608768.
34.Kukangku. (2024). Kukang dilepasliarkan. https://kukangku.id/kliping/kukang-dilepasliarkan-ke-habitatnya-di-lampung/ [Indonesian]
35.Lamichhane, S., Joshi, R., Poudel, B., & Subed, P. (2020). Role of community in leading conservation: effectiveness, success and challenges of a community-based anti-poaching unit in Nepal. Grassroots Journal of Natural Resources, 3(4): 94-109. Doi: https://doi.org/10.33002/nr2581.6853.03046
36.Landim, A.S., Souza, J.M,, dos Santos, L.B., Neto, L.E.M.F, da Silva, D.T., & Ferreira, F.S. (2023). Food taboos and animal conservation: a systematic review on how cultural expressions influence interaction with wildlife species. Journal of Ethnobiology and Ethnomedicine, 19:31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13002-023-00600-9.
37.Lesmana, W.Y., & Abduh, R. (2024). Criminal law policy on the protection of protected wildlife. Jurnal Hukum dan Pranata Sosial Islam, 6 (1): 235-250, DOI: 10.37680/almanhaj.v6i1.5029.
38.Ma’rufia, N., Masy’ud, B., & Sunkar, A. (2019). Keterlibatan perempuan dalam konservasi satwa liar melalui kegiatan penangkaran burung di wilayah Klaten dan Bogor. Jurnal Pengelolaan Sumberdaya Alam dan Lingkungan, 9 (1): 174-181 doi: 10.29244/jpsl.9.1.174-181. [Indonesian].
39.Meppelink, C.S., Smit, E.G., Buurman, B.M., & van Weert, J.C. (2015). Should we be afraid of simple messages? The effects of text difficulty and illustrations in people with low or high health literacy. Health Communication, 30(12):1181-1189. https://doi.org/10.1080/10410236.2015.1037425
40.Mariño, P.J., García, M,, Sanchez, S.L.Z., Mamani-Benito, M.O., Mamani, P.G.R., García, M.S.B., Lozada, R.O., & García, M.W.C. (2024). Psychometric properties of a short academic motivation scale (SAMS) in medical students. Behavior Science,14: 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/ bs14040316.
41.Maryanto, I., Maharadatunkamsi, Achmadi, A.S., Wiantoro. S., Sulistyadi, E., Yoneda, M., Suyanto. A., & Sugardjito, J. (2020). Checklist of the Mammals of Indonesia Scientific, English, Indonesia Name and Distribution Area Table in Indonesia Including CITES, IUCN and Indonesian Category for Conservation. Research Center for Biology Indonesian Institute of Sciences.
42.Mascaro, J.S., Florian, M.P., Ash, M.J., Palmer, P.K., Frazier, T., Condon, P., & Raison, C. (2020). Ways of knowing compassion: How do we come to know, understand, and measure compassion when we see it? Frontiers in Psychology, 11, Article 547241. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.547241.
43.Mendl, M., Neville, V., & Paul, E.S. (2022). Bridging the gap: human emotions and animal emotions. Affec. Sci. 3:703–712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42761-022-00125-6.
44.Miralles A, Raymond M, Lecointre G. (2019). Empathy and compassion toward other species decrease with evolutionary divergence time. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-56006-9.
45.Musavira, M.E., Suparmi, S., & Rahayu, E. (2023). Emotional maturity and resilience with adjustment: correlational study in blind adolescent. Jurnal Psikologi, 12(3):356-361.
46.Nekaris, K.A.I., & Poindexter, S. (2020). Nycticebus hilleri. The IUCN red list of threatened species 2020: e.T163019804A163020000. https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020- 2.RLTS.T163019804A163020000.en.
47.Nekaris, K.A.I., Poindexter, S., Reinhardt, K., Sigaud, M., Cabana, F., Wirdateti, W., & Nijman V. 2017. Coexistence between Javan slow lorises (Nycticebus javanicus) and humans in a dynamic agroforestry landscape in West Java, Indonesia. International Journal of Primatology, 38:303–320. DOI 10.1007/s10764-017-9960-2.
48.Nuraeni, E., Supartono, T., & Deni. (2018). Perdagangan satwa liar jenis kukang (Nycticebus sp) di pasar hewan Plered Kecamatan Weru, Kabupaten Cirebon. Wanaraksa, 12 (1):1-11. https://journal.uniku.ac.id/index.php/wanaraksa/article/view/4541/2672.[Indonesian].
49.Nurhaida, I. 2011. Kontribusi seni peran fotografi pada kampanye anti-rokok melalui perancangan media hiburan fotonovela. Jurnal Seni dan Budaya Panggung, 21(2): 110-123 [Indonesian].
50.Nurhaida, I., Setiawan, A., Bakri, S., & Wiranata, G.A.B. (2011). Pengembangan komik fabel untuk media komunikasi dan suplemen pendidikan lingkungan dalam rangka kampanye pelestarian keanekaragaman hayati di kawasan penyangga Taman Nasional Way Kambas-Lampung, Jurnal Bumi Lestari, 11(2): 331-345.[Indonesian].
51.Nurhaida, I. Harianto, S.P., Junaidi, A., & Syah, P. (2007). Merancang media hiburan buku cergam menjadi media belajar untuk alat bantu komunikasi. Mediator: Jurnal Ilmu Komunikasi, 8(1):51-64, https://doi.org/10.29313/mediator.v8i1. [Indonesian]
52.Nyhus, P.J., Sumianto, & Tilson, R. (2003). Wildlife knowledge among migrants in Southern Sumatra, Indonesia: Implications for conservation. Environmental Conservation, 30(2): 192–199. DOI:10.1017/S0376892903000183.
53.Lakoro, R., Sachari, A., Agung, E.B.W., & Sabana, S. (2019). Design of DRR awareness campaign media by the revitalization of Sundanese oral culture. Advances in Social Science, Education, and Humanities Research, Proceeding of 4th International Conference on Arts Language and Culture (ICALC), 421:363-370.
54.Pardede, E.L., & Venhorst, V.A. (2024). Does ethnicity affect ever-migrating and the number of migrations? The case of Indonesia. European Journal of Population, 40:6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10680-023-09694-z.
55.Poindexter, S.A., Nijman V, Imron, M.A., & Nekaris, K.A.I. (2023). Goal-directed travel in the nocturnal Javan slow loris (Nycticebus javanicus). Ecologies, 4:568–579. https:// doi.org/10.3390/ecologies4030037
56.Ponka T, Kuklien. N., & Sibarani, D.M.N. (2019). The historical influence of the Javanese ethnicity and culture on the political consciousness and mentality of Indonesian people. Proceeding of 4th International Conference on Contemporary Education, Social Sciences and Humanities (ICCESSH) Advances in Social Science, Education and Humanities Research, 329:2171- 2175.
57.Quarles, L.F., Dechanupong, J., Gibson, N., & Nekaris, K.A.I. (2023). Knowledge, beliefs, and experience regarding slow lorises in Southern Thailand: Coexistence in a developed landscape. Animals, 13:3285. https://doi.org/ 10.3390/ani13203285.
58.Ritten, J.C., Bastian, C. & Phillips, O. (2021). The relative effectiveness of law enforcement policies aimed at reducing illegal trade: Evidence from laboratory markets. PLoS ONE, 16(11): e0259254. https://doi.org/10.1371/ journal.pone.0259254.
59.Roy, R., & Kumar, V.(2024).An analysis of illegal wildlife trade with the aid of social media and prevention strategies, Journal of Wildlife and Biodiversity, 8(1), 386-401. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10207005.
60.Rülke, J., Mieckmann, M., Nzau, J.M., & Teucher, M. (2020). How ecocentrism and anthropocentrism influence human-environment relationships in a Kenyan biodiversity hotspot. Sustainability, 12:8213. doi:10.3390/su12198213.
61.Sinaga, R.M. (2021). The kinship commodification of local ethnic in Lampung in multicultural relations. Folklore/Edebyat, 27( 108): 1163 – 1183. DOI: 10.22559/folklor.1846
62.Sarabian, C., Wilkinson, A., Sigaud, M., Kano, F., Tobajas. J., Darmaillacq, A.S., Zikusoka, G.K., Joshua, M., Plotnik, J.M., & MacIntos, A.J.J. (2023). Disgust in animals and the application of disease avoidance to wildlife management and conservation. Journal of Animal Ecology, 1489-1508. DOI: 10.1111/1365-2656.13903.
63.Tobore, T. (2020). Towards a comprehensive theory of love: The quadruple theory. Frontier in Psychology,11:862. Doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00862.
64.Tsortanidou, X., Daradoumis, T., & Barberá-Gregori, E. (2020). Convergence among imagination, social-emotional learning, and media literacy: An integrative literature review. Early Child Development and Care. https://doi.org/10.1080/03004430.2020.1753720.
65.Vedernikova, E., Kuppens, P., & Erbas, Y. (2021). From knowledge to differentiation: Increasing emotion knowledge through an intervention increases negative emotion differentiation. Frontier in Psychology, 12:703757. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.703757.
66.Vucetich, J.A., Macdonald, E.A., Burnham, D., Bruskotter, J.T., Johnson, D.D.P., & Macdonald, D.W. (2021). Finding purpose in the conservation of biodiversity by the commingling of science and ethics. Animals, 11: 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/ ani11030837.
67.WCS Indonesia. (2024). Overview Forest Program. Forest Program (wcs.org).
68.Withaningsih, S., Parikesit, Ayundari, A., Prameswari, G., Erri, N., Megantarc, E.N., & Husodo, T. (2019). Distribution and habitat of Javan slow loris (Nycticebus javanicus É. Geoffroy, 1812) in non-conservation areas. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 060006 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5061915.
69.Wojnarowski, K., Podobi’nski, P., Cholewi´nska, P., Smoli´nski, J., & Dorobisz, K. (2021). Impact of estrogens present in environment on health and welfare of animals. Animals, 11:2152. https:// doi.org/10.3390/ani11072152
70.Wulandari, C., Bakri, S., Riniarti, M., & Supriadi, S. (2021). Fostering the sustainability of community forestry program: A case study in
Lampung-Sumatra. Forestry Ideas, 27 (1):210-232.
71.Yollanda, W. & Jeffrey, K. (2020). Effectiveness of the convention on international trade in endangered species of wild fauna and flora (CITES) in curbing elephant poaching in Zimbabwe. IAR Journal of Business Management, 1(1):38-49. https://www.iarconsortium.org/journal-info/IARJBM
Authors
Copyright (c) 2026 Jurnal Manajemen Hutan Tropika

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Jurnal Manajemen Hutan Tropika is an open access journal which means that all contents is freely available without charge to the user or his/her institution. Users are allowed to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts of the articles in this journal without asking prior permission from the publisher or the author. This is in accordance with the Budapest Open Access Initiative (BOAI) definition of open access.