Regenerative Tourism in the Philippines: Millennial Tourists’ Perspective and Intent to Participate
Abstract
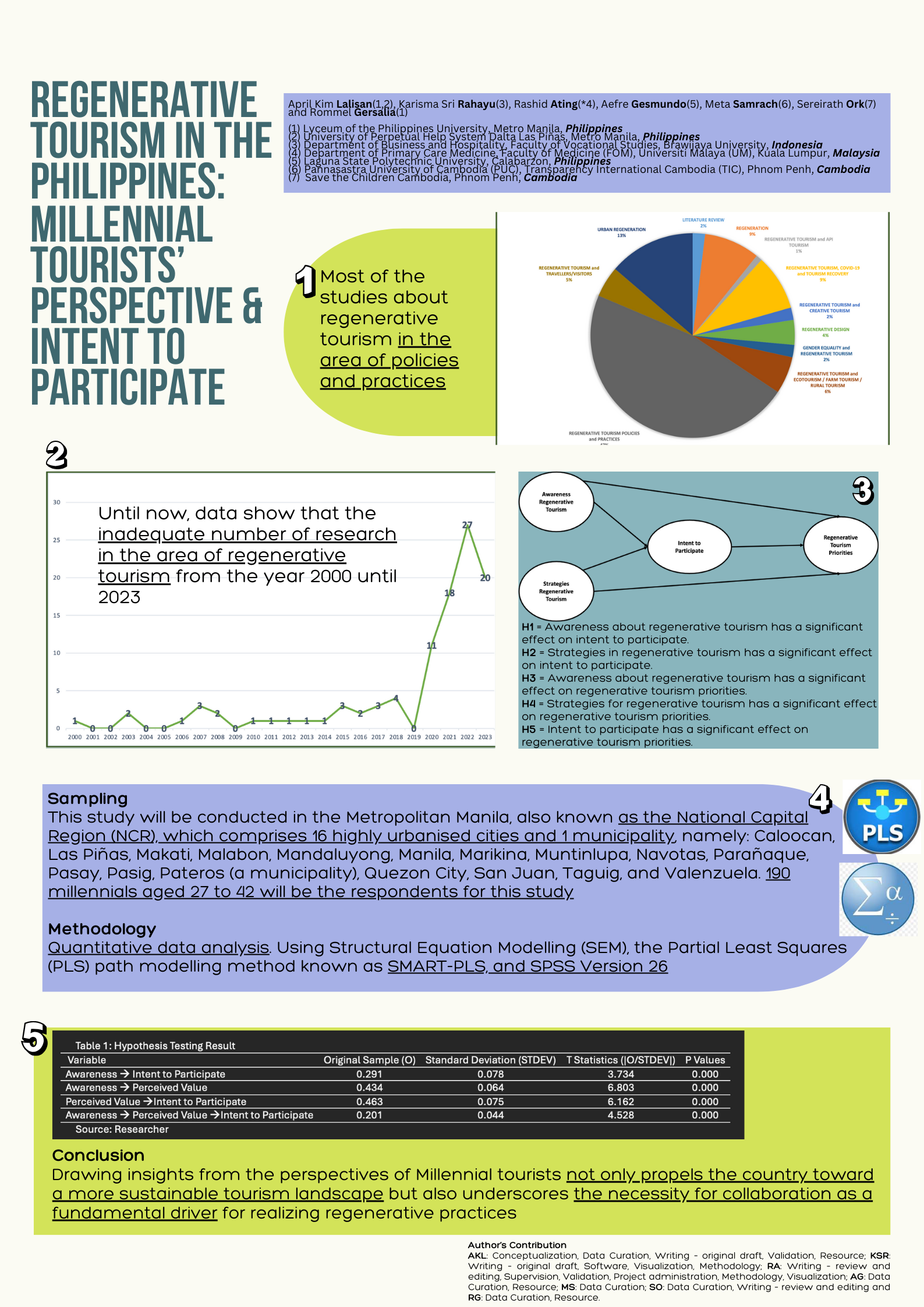
Tourism development can put destinations on a more equitable and environmentally friendly path by applying regenerative principles to tourism development. The millennial generation, known as sustainability-conscious consumers, bears much potential to participate in regenerative tourism. This study aimed to determine the awareness, perceived value, and intent to participate in regenerative tourism of the millennial generation in the Philippines in Metropolitan Manila and the surrounding areas such as Bulacan, Cavite, Angeles City, Cavite, Laguna, and others. This type of research is explanatory research, conducted through direct surveys of 190 millennial Filipinos through online questionnaires. Data was analyzed using SEM-PLS. The results of this study provide insights into the readiness of the millennial generation to participate in regenerative tourism practices. This research intends to contribute theoretically to tourism readiness and recovery post-pandemic. Moreover, it can make a practical contribution to tourism stakeholders to support the regenerative and sustainable development of tourist destinations in the Philippines.
Full text article
References
2. International Labour Organization. The Future of Work in The Tourism Sector: Sustainable and Safe Recovery and Decent Work in The Context of The COVID-19 Pandemic https://www.ilo.orgOnline: https://www.ilo.org/wcmsp5/groups/public/---ed_dialogue/---sector/documents/meetingdocument/wcms_840403.pdf, 2022.
3. United Nations World Tourism Organization. Tourism on Track for Full Recovery as New Data Shows Strong Start to 2023 https://www.unwto.org Online:https://www.unwto.org/news/tourism-on-track-for-full-recovery-as-new-data-shows-strong-start-to-2023, 2023.
4. International Monetary Fund. Tourism Recovery Halfway to Pre-Pandemic Levels https://www.imf.org Online: https://www.imf.org/-/media/Files/Countries/ResRep/pis-region/tourism-tracker/2023q1-apd-tourism-tracker.ashx, 2023.
5. United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization World Heritage Convention. Experts Call for Inclusive and Regenerative Tourism to Build Back Stronger Post-COVID-19 https://whc.unesco.org Online: https://whc.unesco.org/en/news/2177, 2020.
6. Center for Responsible Travel. The Case for Responsible Travel: Trends & Statistics 2019 https://www.responsibletravel.org Online: https://www.responsibletravel.org/wp-content/uploads/sites/213/2021/03/trends-and-statistics-2019.pdf, 2021.
7. Postma, A. Regenerative Tourism: The Next Step in Sustainable Tourism CBI Ministry of Foreign Affairs Online: https://www.cbi.eu/news/regenerative-tourism-next-step-sustainable-tourism, 2021.
8. Lethabo-Thabo, R. N. d. What are the Benefits of Regenerative Travel & Tourism? World Travel & Tourism Council Online: https://travelhub.wttc.org/blog/what-is-regenerative-travel.
9. Suárez-Rojas, C.; Hernández, M. M. G.; León, C. J. Sustainability in Whale-Watching: A Literature Review and Future Research Directions based on Regenerative Tourism. Tourism Management Perspectives, 2023, 47, 101120.
10. The European Sting. The Future of Tourism is Sustainable and Regenerative https://europeansting.com Online: https://europeansting.com/2023/09/13/the-future-of-tourism-is-sustainable-and-regenerative/, 2023.
11. Lane, L. Six Tourist-Dependent Countries that Would Benefit Most from 'Regenerative Travel' Forbes Online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/lealane/2021/08/12/six-tourist-dependent-countriesthat-would-benefit-most-from-regenerative-travel/?sh=32dc81302c11, 2021.
12. De Castro, H. The Ripple Effect of Regenerative Tourism: A Sustainable Wave of Change LinkedIn Online: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/ripple-effect-regenerative-tourism-sustainablewave-change-de-castro-mkwoe, 2023.
13. Glusac, E. Move Over, Sustainable Travel. Regenerative Travel Has Arrived New York Times Online: https://www.nytimes.com/2020/08/27/travel/travel-future-coronavirus-sustainable.html, 2020.
14. McEnhill, L.; Jorgensen, E. S.; Urlich, S. C. Paying it Forward and Back: Regenerative Tourism as Part of The Place Centre of Excellence for Sustainable Tourism Internal Report 2020/101 Lincoln University, 2020.
15. Laurent, M. Regenerative Tourism Will Be at The Forefront of The Recovery Effort EHL Insights Online: https://hospitalityinsights.ehl.edu/regenerative-tourism, 2021.
16. Lethabo-Thabo, R n.d. What are The Benefits of Regenerative Travel & Tourism? World Travel & Tourism Council Online: https://travelhub.wttc.org/blog/what-is-regenerative-travel.
17. Rocamora, J. A. L. 'Regenerative' Tourism to Help Recovery Route Philippine News Agency Online: https://www.pna.gov.ph/articles/1141625, 2021.
18. Dimock, M. Defining Generations: Where Millennials End and Generation Z Begins Pew Research Online: https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2019/01/17/where-millennials-end-and-generation-z-begins/, 2019.
19. Jasrotia, A.; Choudhary, P.; Kour, P.; Yadav, V. Exploring the Motivations of Millennials Opting for Temple Stays in India. International Journal of Religious Tourism and Pilgrimage, 2021.
20. Kent State University n.d. How Millennials are Steadily Impacting The Hotel, Foodservice, and Hospitality Industries https://www.kent.edu Online: https://www.kent.edu/ehhs/fla/hm/millennial-generation.
21. Sharmin, F.; Sultan, M. T.; Badulescu, A.; Bac, D. P.; Li, B. Millennial Tourists' Environmentally Sustainable Behavior Towards A Natural Protected Area: An Integrative Framework. Sustainability, 2020, 12(20) 8545.
22. Gao, Y n.d. Sustainable tourism among millennials: from awareness to action.
23. Indra, C. The Art of Responsible Tourism: Travelers Can be A Force for Good Forbes Online:https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbesbusinesscouncil/2023/08/25/the-art-of-responsible-tourism-travelers-can-be-a-force-for-good/?sh=7369f8b026a5, 2023.
24. Tham, A.; Sharma, B. Regenerative Tourism: Opportunities and Challenges. Journal of Responsible Tourism Management, 2023, 3(1) 15-23.
25. Zaman, U.; Aktan, M.; Agrusa, J.; Khwaja, M. G. Linking Regenerative Travel and Residents' Support for Tourism Development in Kaua'i Island (Hawaii): Moderating-Mediating Effects of Travel-Shaming and Foreign Tourist Attractiveness. Journal of Travel Research, 2023, 62(4), 782-801.
26. United Nations n.d. The 17 goals Online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals.
27. Owen, C. Regenerative Tourism: A Case Study of The Resort Town. Yulara Open House International, 2007, 32(4), 42-53.
28. Ajoon, E.; Rao, Y. A Study on The Consciousness of Young Travelers Towards Regenerative Tourism: Regarding Puducherry Online: http://tourismleaderssummit.org/jtear, 2020, 4(1).
29. Bellato, L.; Frantzeskaki, N.; Nygaard, C. A. Regenerative Tourism: A Conceptual Framework Leveraging Theory and Practice. Tourism Geographies, 2023, 25(4), 1026-1046.
30. CBI Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Regenerative Tourism: Moving Beyond Sustainable and Responsible Tourism https://www.cbi.eu Online: https://www.cbi.eu/market-information/tourism/regenerative-tourism, 2022.
31. Duxbury, N.; Bakas, F. E.; Vinagre de Castro, T.; Silva, S. Creative Tourism Development Models Towards Sustainable and Regenerative Tourism. Sustainability, 2020, 13(1), 2.
32. Mehrabian, A.; Russell, J. A. An approach to environmental psychology. The MIT Press, 1974.
33. Arakaki, M. 'Regenerative' Tourism Makes Visitors more Attractive to Residents University of Hawai'i Online: https://www.hawaii.edu/news/2022/07/11/regenerative-tourism-visitors/, 2020.
34. King, C. Beyond Sustainability: A Global Study of Nature-Based Solutions in Regenerative Tourism Travel and Tourism Research Association: Advancing Tourism Research Globally 38 https://scholarworks.umass.edu/ttra/2022/researchabstract/38, 2022.
35. Dredge, D. Regenerative Tourism: Transforming Mindsets, Systems and Practices. Journal of Tourism Futures, 2022, 8(3), 269-281.
36. Nieves-Pavón, S.; López-Mosquera, N.; Jiménez-Naranjo, H. The Factors Influencing STD Through SOR Theory. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 2023, 75, 103533.
37. Kusumawati, A.; Rahayu, K. S.; Putra, E. W. Antecedents Customer Decision to Visit Yogyakarta As Special Regions in Indonesia. Cogent Business & Management, 2022, 9(1), 2050062.
38. Philippines Statistics Authority. National quickstart for 2023 Republic of the Philippines Online: https://psa.gov.ph/statistics/quickstat/national-quickstat/all/*34a, 2023.
39. Philippines Statistics Authority. Republic of the Philippines NCR Provincial Office (Cities of Manila, Mandaluyong, and San Juan) Online: https://rssoncr.psa.gov.ph/ncr1, 2023.
Authors
Media Konservasi is an open access journal, meaning that all content is freely available without charge to the user or their institution. Users are allowed to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts of the articles in this journal without needing to request prior permission from the publisher or the author.
All articles published by Media Konservasi are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. This allows for unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided proper credit is given to the original authors.
Authors submitting manuscripts should understand and agree that the copyright of published manuscripts is retained by the authors. Copyright encompasses the exclusive rights of authors to reproduce, distribute, and sell any part of the journal articles in all forms and media. Reproduction of any part of this journal, its storage in databases, and its transmission by any form or media is allowed without written permission from Media Konservasi.